boric acid gold refining


Introduction to Boric Acid Gold Refining
Boric acid gold refining is a lesser-known but highly effective method used in the purification of gold. Boric acid, a weak acid made from boron, is commonly used in industrial applications, including glassmaking and as an insecticide. However, its unique properties make it an excellent flux in the gold refining process. This method is often used as a safer alternative to traditional gold refining processes that involve toxic chemicals like mercury and cyanide. The use of boric acid helps simplify the gold purification process while making it more environmentally friendly.
How Boric Acid Works in Gold Refining
Boric acid plays a critical role in the gold refining process by acting as a flux. A flux is a material that helps to purify metal by melting impurities and allowing them to be separated from the metal itself. In the case of boric acid gold refining, it helps to lower the melting point of gold, making the smelting process more efficient and allowing for the removal of unwanted materials from the gold.
The Role of Boric Acid as a Flux
The main purpose of boric acid in gold refining is to act as a flux to clean the gold and remove impurities. When mixed with the gold ore and heated, boric acid forms a glass-like compound that traps impurities and facilitates their removal. This process helps produce higher-purity gold, ensuring a better-quality end product. By lowering the melting point of gold, boric acid speeds up the refining process, which reduces the amount of energy needed and makes the process more cost-effective.


Advantages of Using Boric Acid in Gold Refining
Boric acid gold refining has several advantages over traditional refining methods. These benefits make it an attractive option for small-scale miners and refiners who are looking for a safer and more efficient way to purify gold.
Environmentally Friendly
One of the primary advantages of using boric acid in gold refining is that it is more environmentally friendly than traditional methods. Unlike mercury and cyanide, which are toxic and pose significant environmental risks, boric acid is much safer to use and handle. It breaks down more easily in nature, reducing the chances of long-term environmental contamination. This makes boric acid a much more sustainable option for gold refiners who are concerned about the ecological impact of their work.
Cost-Effective Refining
Boric acid gold refining is also a cost-effective method. The use of boric acid helps reduce the amount of energy required to melt gold, which can significantly lower operational costs. Additionally, boric acid is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a practical choice for small-scale refiners who are working with limited resources. The simplicity of the process also helps minimize labor and equipment costs.
Safer for Workers
Gold refining using boric acid is much safer for workers than methods that involve the use of hazardous chemicals. Cyanide and mercury, for example, are highly toxic substances that can lead to serious health problems if not handled properly. By switching to boric acid, gold refiners can reduce the health risks for workers and create a safer work environment. The reduced toxicity of boric acid means there is less risk of chemical exposure and fewer safety precautions are required, making the process simpler and more manageable.
The Boric Acid Gold Refining Process
The process of refining gold with boric acid is straightforward and requires minimal equipment, making it accessible for small-scale miners. It involves a few basic steps, all of which can be carried out with readily available tools.
Preparing the Gold Ore
Before beginning the boric acid gold refining process, the gold ore must first be crushed into a fine powder. This helps to increase the surface area of the gold, allowing the boric acid to more effectively bind with impurities. Once the ore is crushed, it is mixed with boric acid in preparation for smelting.
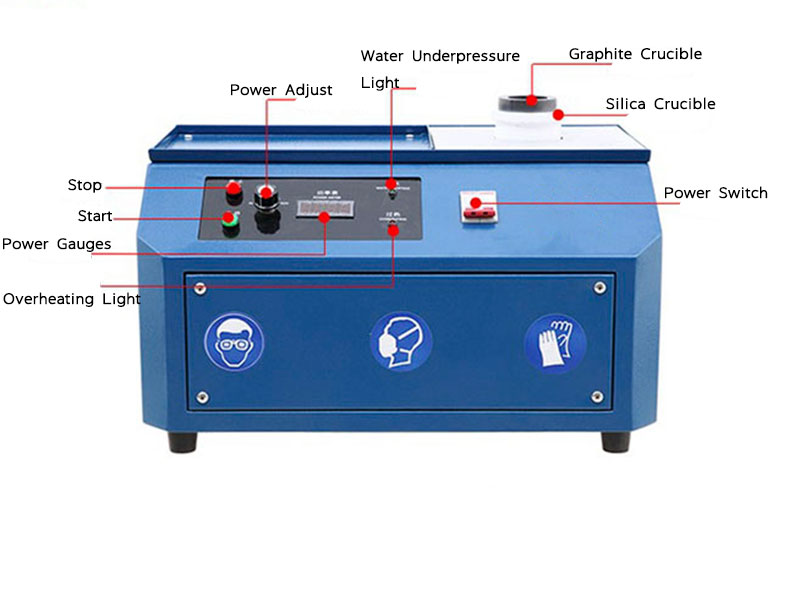
Smelting the Gold
The mixture of gold ore and boric acid is then placed into a heat-resistant container, such as a crucible, and heated to a high temperature. During this smelting process, the boric acid helps to lower the melting point of the gold, making it easier to separate the metal from impurities. The boric acid also forms a glassy slag that traps these impurities, leaving the pure gold behind.
Removing Impurities
As the mixture heats, the impurities rise to the surface in the form of slag, which can then be skimmed off. Once the refining process is complete, the molten gold is allowed to cool and solidify. After cooling, the slag can be removed, and the refined gold is collected.
Comparing Boric Acid to Other Gold Refining Methods
Boric acid gold refining offers several advantages over traditional methods like the use of mercury or cyanide, but it is also important to understand how it compares to other modern refining techniques.
Safer Than Mercury and Cyanide
The use of mercury and cyanide in gold refining is a well-established practice, but it is also fraught with risks. Mercury is highly toxic and poses severe health risks to miners and the environment, while cyanide can cause catastrophic environmental damage if not handled properly. Boric acid, on the other hand, is a much safer alternative. It is not nearly as toxic as mercury or cyanide, and the risks of accidental exposure are much lower. This makes boric acid gold refining a more responsible choice for refiners who want to minimize health and environmental risks.
More Accessible Than Advanced Methods
Boric acid gold refining is more accessible than some of the more advanced gold refining techniques that require expensive equipment and chemicals. Methods like electrorefining or the Miller process, for instance, are highly effective but require specialized equipment and expertise. Boric acid gold refining, on the other hand, can be performed with basic tools and equipment, making it an ideal choice for small-scale miners or those working in remote locations.
Boric acid gold refining is an effective, cost-efficient, and safer alternative to traditional gold purification methods that involve toxic chemicals. By acting as a flux, boric acid helps to lower the melting point of gold and remove impurities, resulting in high-purity gold with fewer contaminants. The method is not only safer for workers but also more environmentally friendly, making it an ideal solution for small-scale miners and refiners who are looking to refine gold responsibly. As awareness of the benefits of boric acid gold refining grows, it is likely to become an increasingly popular choice for gold purification across the globe.