collecting ans smelting gold

Collecting and Smelting Gold
Collecting and smelting gold is an age-old practice that has fascinated humans for centuries. Whether as a hobby or a profession, the allure of gold has driven people to explore, gather, and refine this precious metal from various sources. Understanding the process of collecting gold and the techniques used in smelting it is essential for anyone looking to turn raw gold materials into valuable bullion or jewelry. This article will delve into the steps involved in collecting and smelting gold, exploring the methods, tools, and precautions necessary for successful gold recovery.

Collecting Gold: Sources and Methods
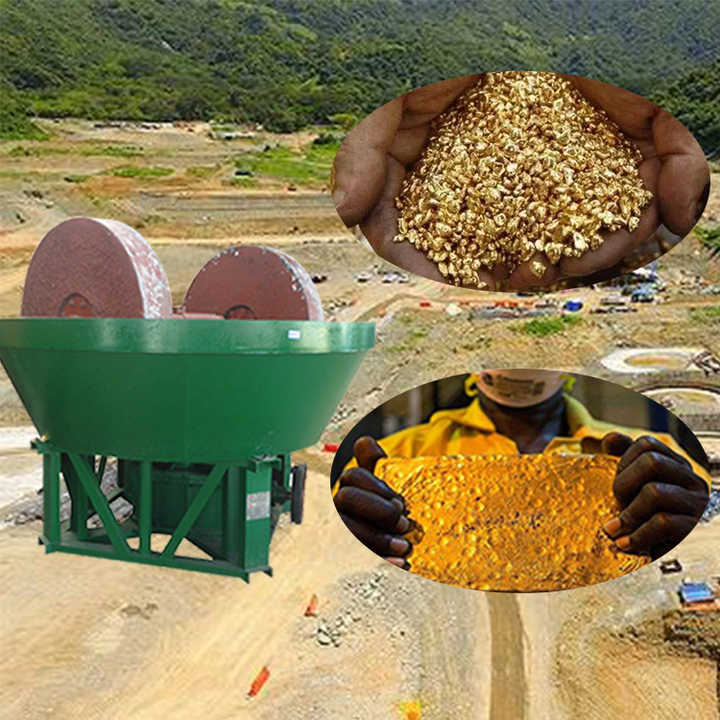
Gold can be collected from several different sources, each requiring a unique approach to extraction. The most common methods of gold collection include panning, dredging, and the recovery of scrap gold. Let’s explore these in detail:
1. Gold Panning
Gold panning is one of the simplest and most accessible methods of collecting gold. It involves using a pan to sift through riverbed sediments in search of small gold particles. This method has been used for centuries and requires minimal equipment, making it a popular choice for amateur gold collectors.
- How it works: Gold panning involves filling a pan with riverbed material, submerging it in water, and then gently swirling the mixture. The lighter materials wash away while the heavier gold settles at the bottom of the pan.
2. Dredging
Dredging is a more advanced method of gold collection, often used by commercial operations. It involves using large machines to remove sediment from the bottom of rivers or streams, extracting gold that has accumulated in these areas over time.
- How it works: A dredge sucks up sediment from the riverbed and passes it through a sluice box, where heavier materials like gold are separated from lighter debris. Dredging is particularly effective in areas with rich gold deposits.
3. Collecting Scrap Gold
Another way to collect gold is by recovering it from old or discarded items, such as jewelry, electronic components, or industrial materials. Scrap gold recovery has gained popularity in recent years due to the increasing value of gold.
- How it works: Scrap gold is collected, melted down, and then refined to separate pure gold from other metals. This process often involves smelting, which we will discuss in more detail later.

Smelting Gold: The Refining Process
Once gold is collected, whether from natural sources or scrap materials, it must be refined through smelting to remove impurities and achieve higher purity levels. Smelting is the process of heating the collected gold to a high temperature, causing it to melt and separate from impurities, such as dirt, minerals, and other metals.
1. Preparing the Gold for Smelting
Before smelting, it is essential to thoroughly clean and prepare the collected gold. This may involve washing, crushing, or sorting the material to remove any non-metallic impurities. For scrap gold, removing other metals like copper, nickel, or silver is crucial for achieving high-purity gold.
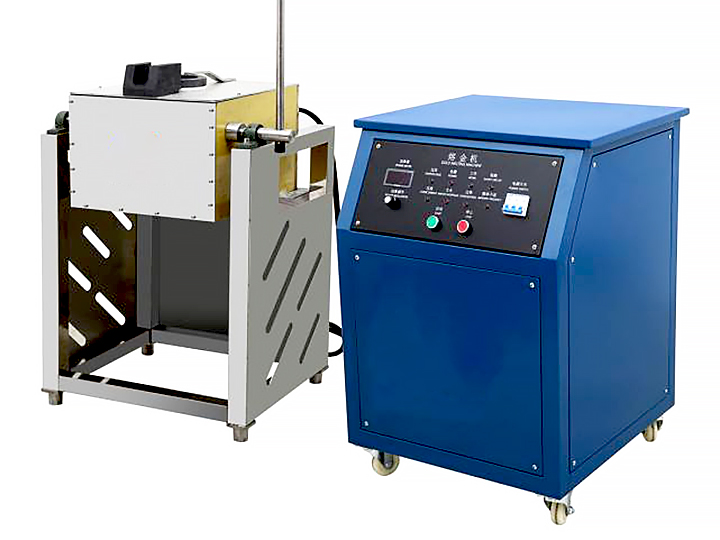
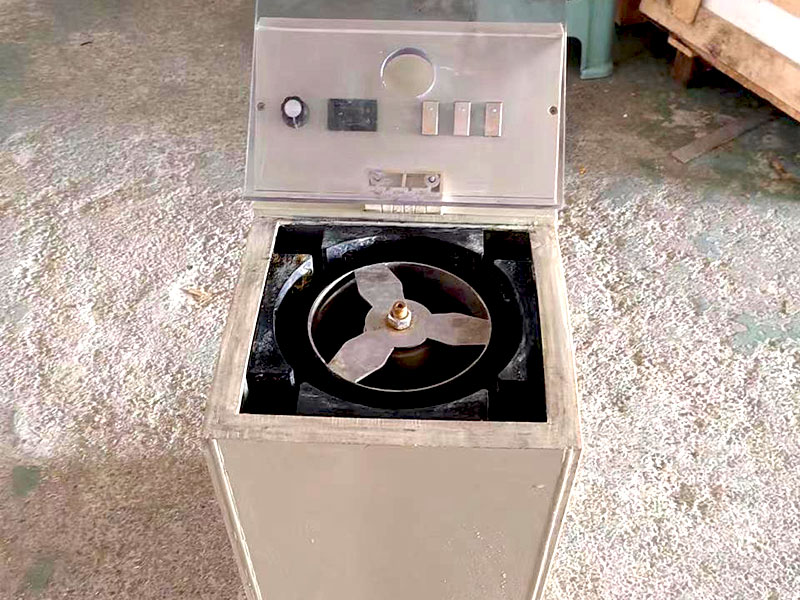
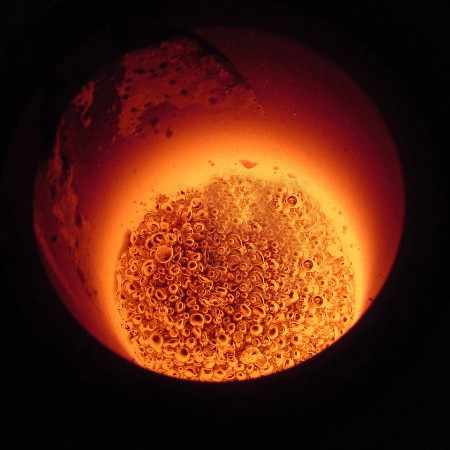
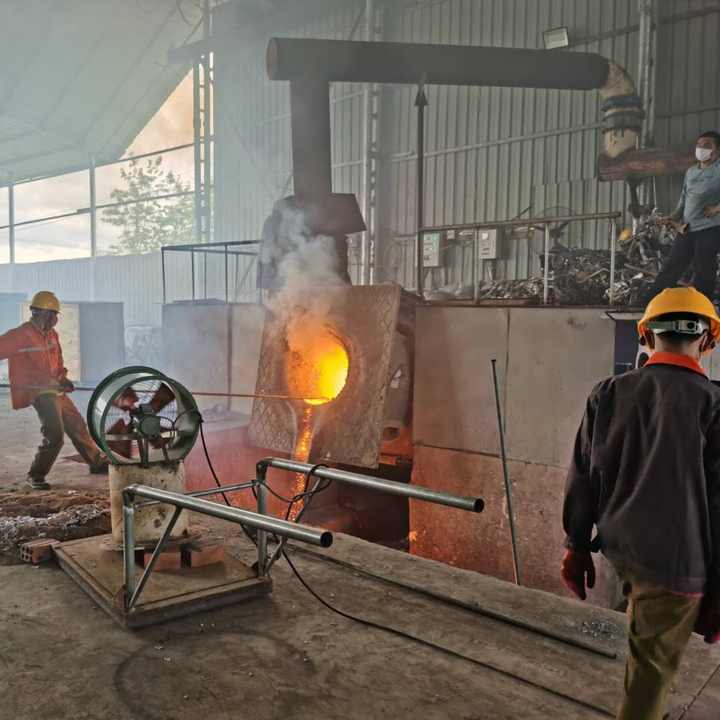
2. The Smelting Process
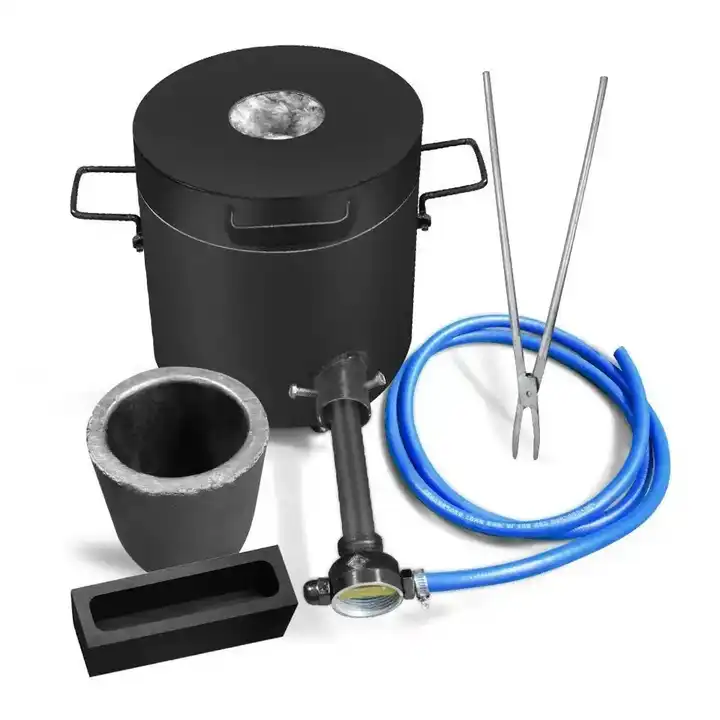
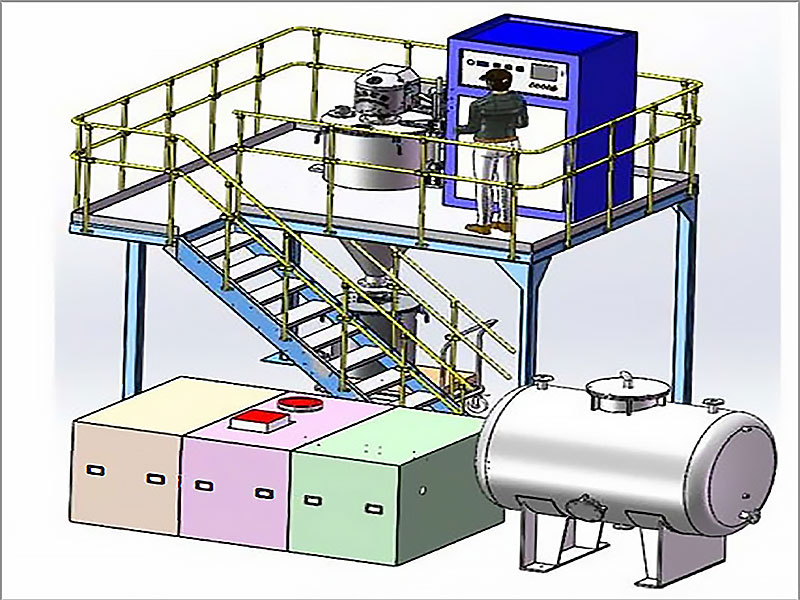
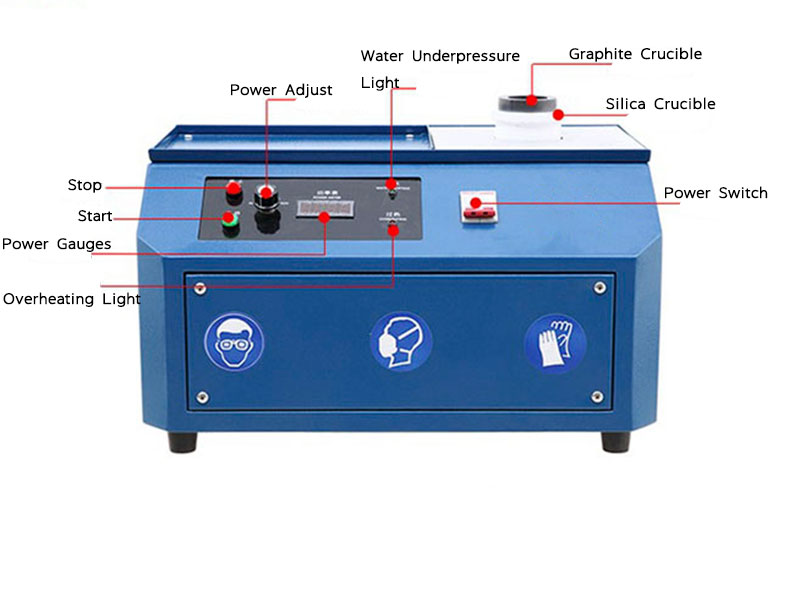
Smelting involves heating gold to its melting point, which is 1,064°C (1,947°F). This can be done in a furnace or with the use of a crucible and blowtorch for smaller-scale operations.
- Tools needed: A furnace or blowtorch, a crucible (a heat-resistant container to hold the gold), and flux (a substance like borax or soda ash used to bind impurities).
- How it works: The gold is placed in the crucible, along with the flux. When the mixture is heated, the gold melts, while the flux binds with the impurities. The impurities rise to the surface as slag, leaving behind the molten gold.
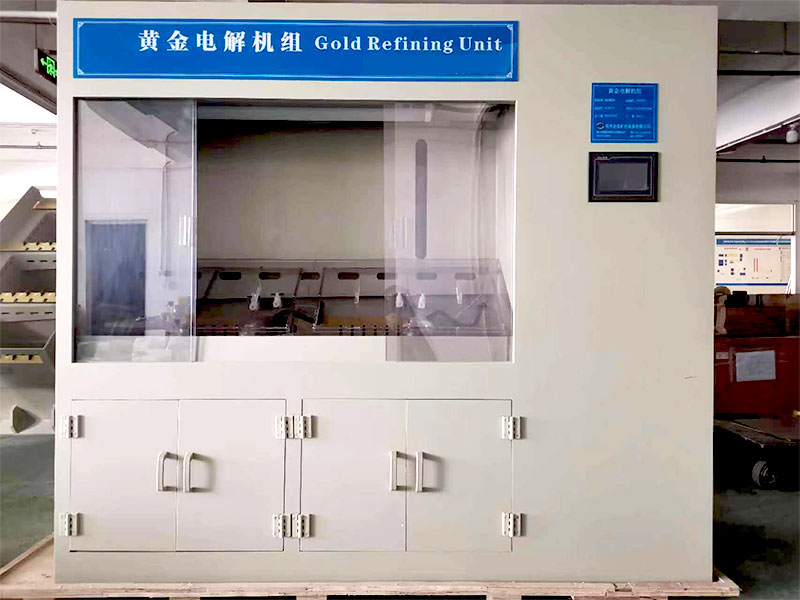
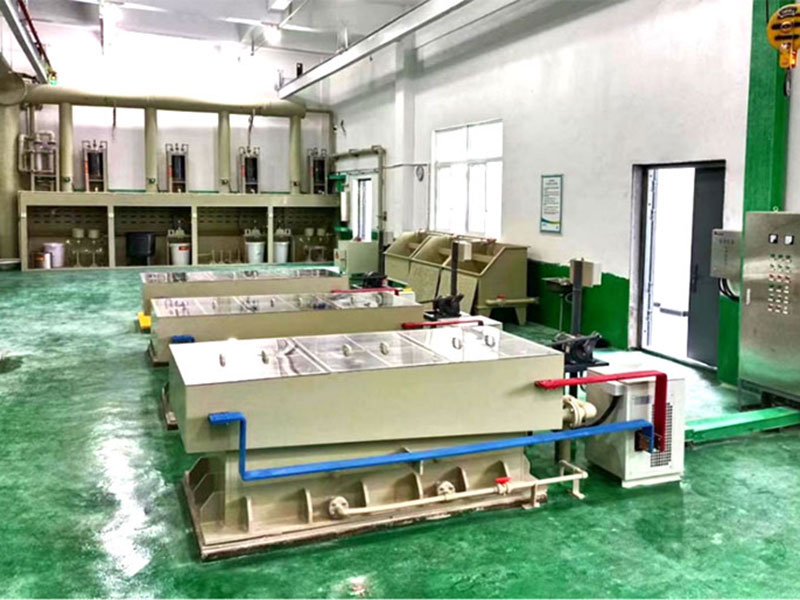
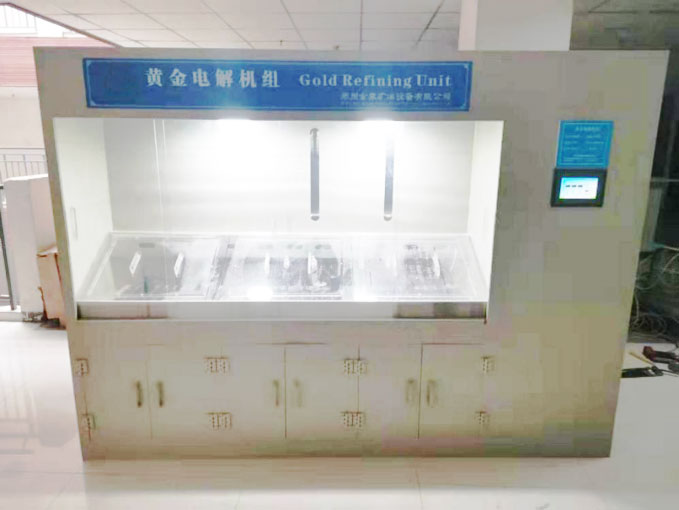
3. Refining the Gold
After smelting, the gold may need further refining to remove any remaining impurities and increase its purity. This is often done through chemical processes like aqua regia, which dissolve the gold and separate it from other metals.
- Refining tools: Chemical solutions, such as nitric acid or hydrochloric acid, and a refining container.
- How it works: The dissolved gold is precipitated out of the solution using chemicals like sodium metabisulfite. The resulting gold powder is then melted again to produce pure gold bullion.
Safety Considerations in Gold Smelting
Gold smelting involves handling high temperatures and potentially hazardous chemicals, so safety precautions are essential. Always wear protective gear, including heat-resistant gloves, goggles, and a face shield. Ensure you work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling toxic fumes generated during smelting.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation is critical to remove harmful gases, especially when working with chemicals like acids.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Heat-resistant gloves, eye protection, and a protective apron are essential to prevent burns and injuries.
Tools and Equipment for Collecting and Smelting Gold
To successfully collect and smelt gold, you will need a variety of tools and equipment. Some of the most common items used in gold smelting include:
- Gold pans and sluice boxes for panning and dredging.
- Metal detectors to locate gold deposits in the ground.
- Crucibles and blowtorches for melting gold.
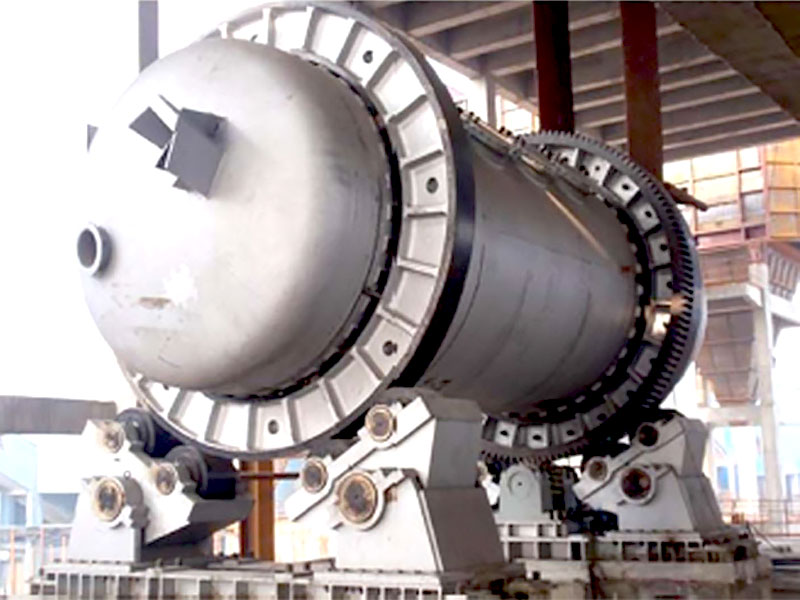
- Furnaces for larger-scale smelting operations.
- Fluxes, such as borax and soda ash, to help remove impurities.
- Refining chemicals like aqua regia for purifying gold.
Collecting and smelting gold is a rewarding process that has been practiced for thousands of years. Whether you are panning for gold in a river, dredging for deposits, or recovering gold from scrap materials, understanding the smelting process is crucial for turning raw gold into valuable, pure bullion. By using the right tools, taking necessary safety precautions, and mastering the techniques of smelting, you can successfully refine and enjoy the beauty and value of gold.