direct smelting of gold
Direct Smelting of Gold: A Simple and Efficient Gold Recovery Method
Direct smelting of gold is an alternative method for recovering gold from raw ore or concentrates without the use of mercury or other chemicals. This process is increasingly popular among artisanal and small-scale miners as it is both environmentally friendly and cost-effective. In this article, we will explore the direct smelting of gold, the advantages of this method, and the steps involved in the process.
What is Direct Smelting of Gold?
Direct smelting is a process in which raw gold ore or concentrate is heated at high temperatures in the presence of a flux, allowing the gold to melt and separate from other impurities. Unlike other methods, such as amalgamation with mercury, direct smelting does not involve any toxic chemicals, making it a safer and more sustainable alternative.
This method is especially valuable in areas where mercury use is banned or where the health and environmental risks of traditional smelting techniques are too high. Direct smelting allows miners to efficiently recover gold using simple equipment and minimal costs.
The Process of Direct Smelting
The direct smelting process involves the following steps:
1. Crushing and Grinding
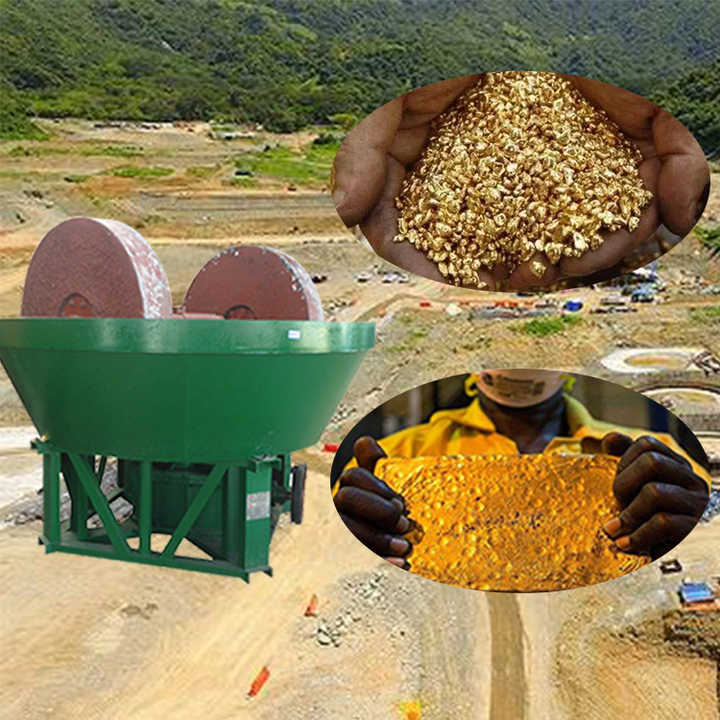
The first step in direct smelting is to crush and grind the gold ore into fine particles. This increases the surface area of the material, making it easier to extract gold during the smelting process. Miners typically use manual tools or small crushers for this step, depending on the scale of the operation.
2. Concentration
Once the ore is crushed and ground, it is then concentrated to separate gold from other materials such as sand, rocks, and minerals. Concentration can be achieved using gravity-based methods such as panning, sluicing, or using a shaking table. The concentrated material is then prepared for the smelting process.
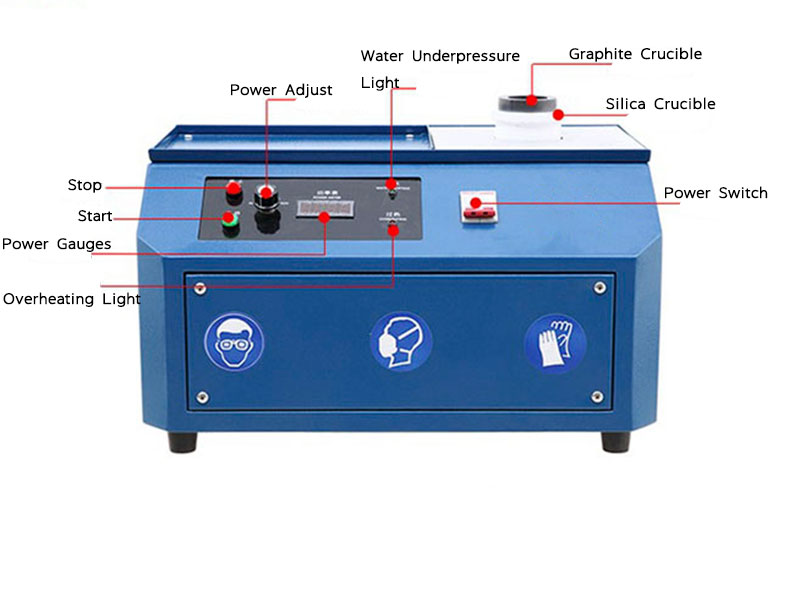
3. Adding Flux
Flux is an essential material used in the direct smelting process. Flux helps lower the melting point of the materials, allowing the gold to melt more easily. Common fluxes used in gold smelting include borax, sodium carbonate, and silica. These substances help bind with the impurities in the concentrate, separating them from the molten gold during the smelting process.
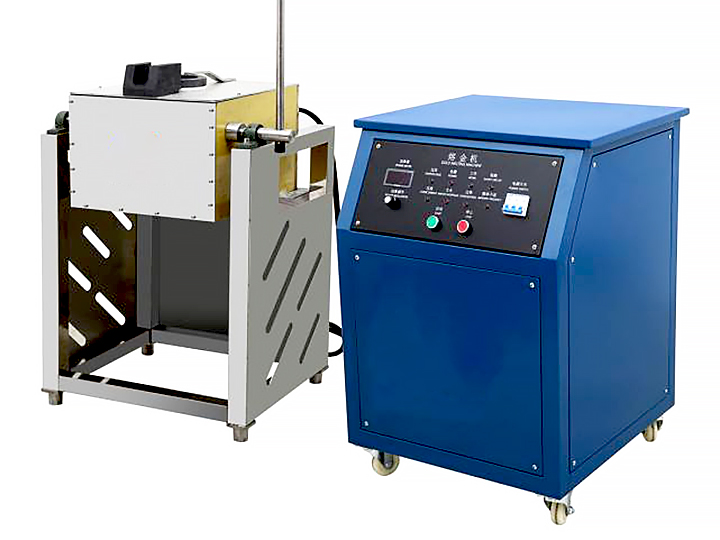
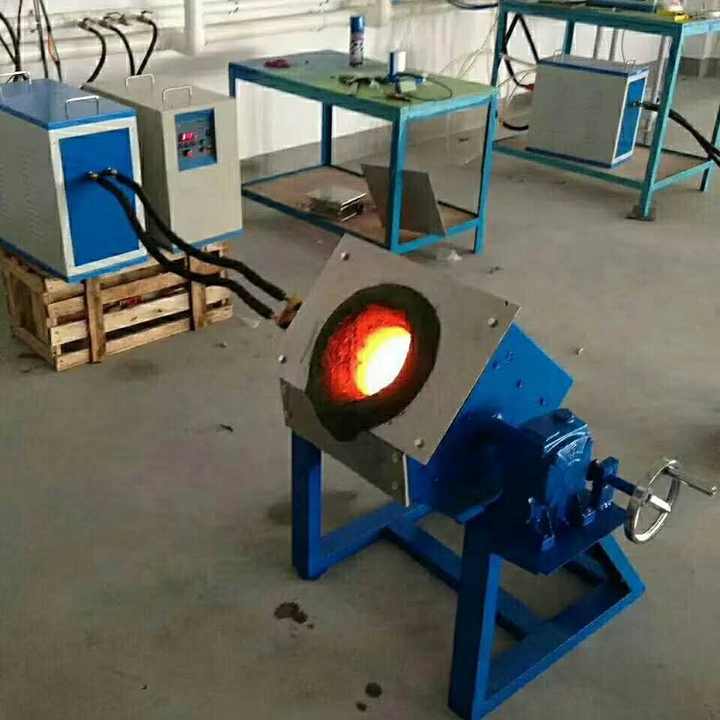
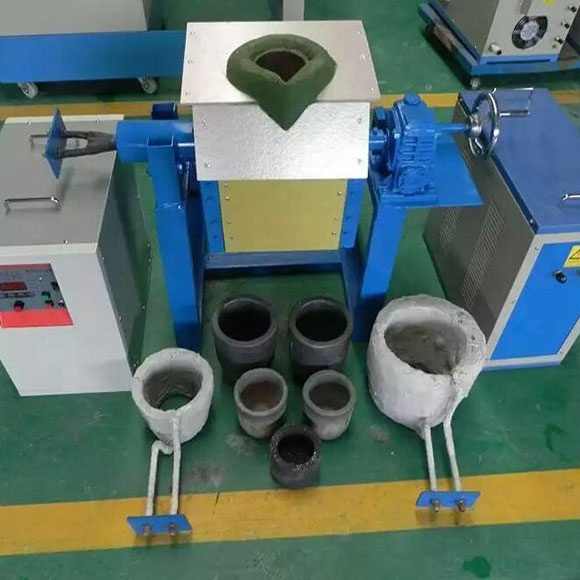
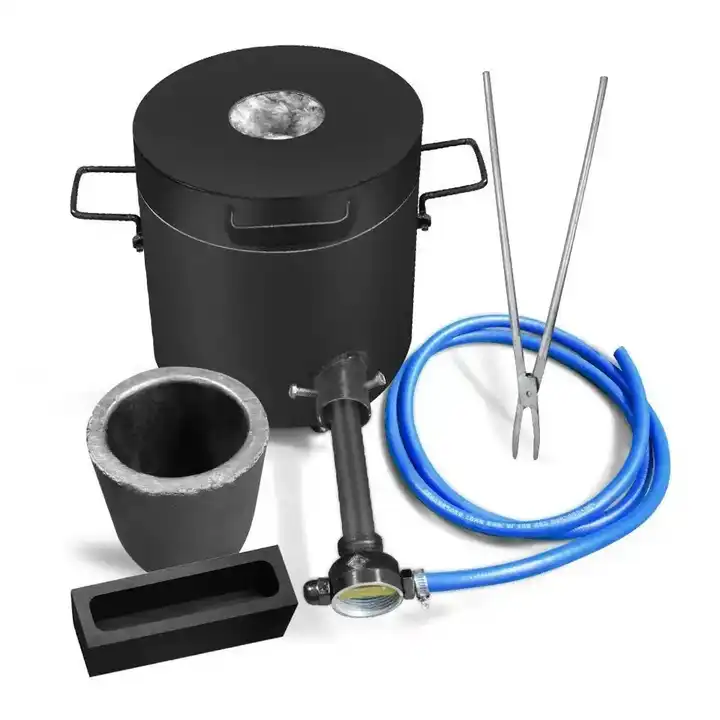
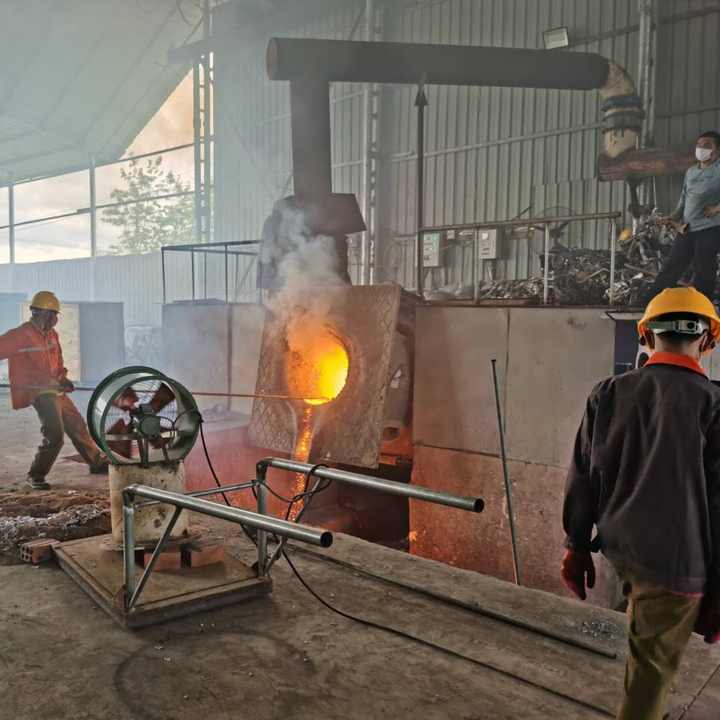
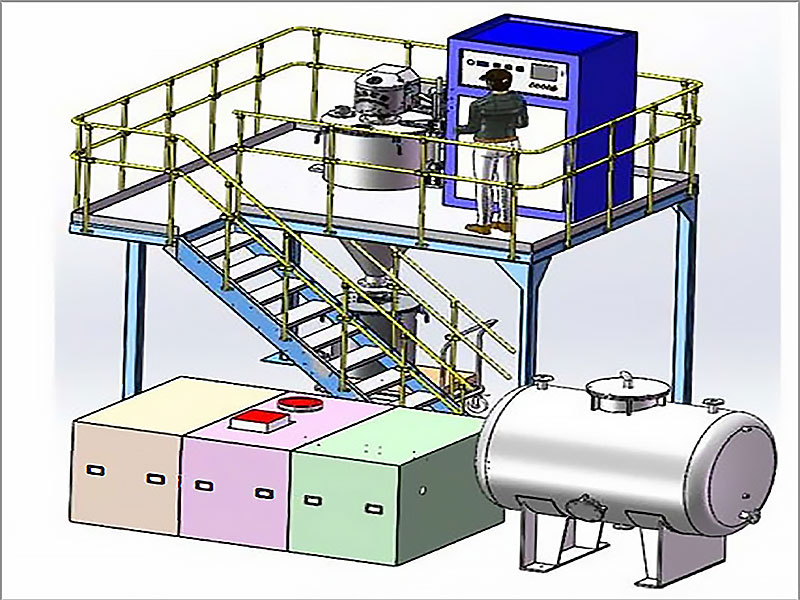
4. Smelting
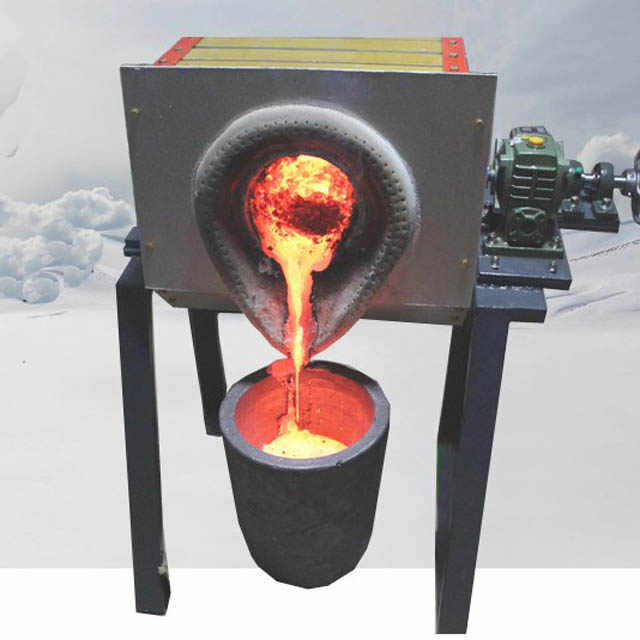
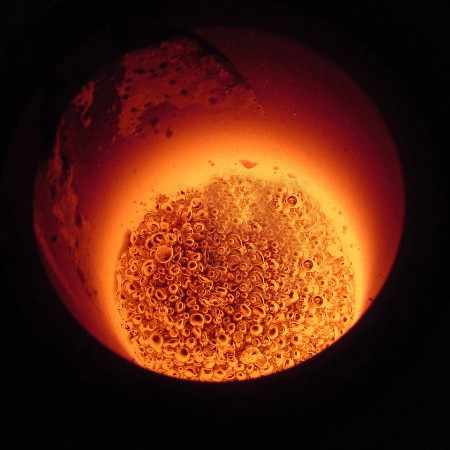
The prepared gold concentrate and flux are placed in a crucible or smelting pot and heated at extremely high temperatures, typically around 1,100°C (2,012°F). This can be done using a small furnace or even a simple fire fueled by charcoal or propane. As the mixture heats, the gold melts and collects at the bottom of the crucible while impurities rise to the top as slag.
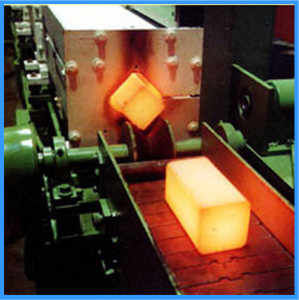
5. Pouring and Cooling
Once the gold is fully melted, the molten material is poured into molds and allowed to cool. The result is a gold ingot or nugget that is ready for further refining or sale. The slag, which contains the impurities, is discarded.
Advantages of Direct Smelting of Gold
Direct smelting offers several advantages over traditional gold recovery methods:
1. Mercury-Free
One of the most significant benefits of direct smelting is that it does not involve mercury, which is often used in artisanal and small-scale gold mining. Mercury is highly toxic and poses severe health risks to miners, local communities, and the environment. Direct smelting eliminates this hazard entirely.
2. Cost-Effective
Direct smelting is a relatively low-cost process. The equipment required is simple and inexpensive, making it an attractive option for small-scale miners with limited resources. Additionally, because it does not rely on chemicals like cyanide or mercury, operating costs are lower.
3. Environmentally Friendly
By eliminating the use of toxic chemicals, direct smelting reduces the environmental impact of gold mining. Mercury and cyanide, commonly used in traditional gold recovery processes, can contaminate water sources and harm local ecosystems. Direct smelting provides a cleaner and safer alternative.
4. High Gold Recovery Rates
Despite its simplicity, direct smelting is an efficient process that yields high gold recovery rates. Miners can achieve up to 95% gold recovery using this method, making it a reliable option for small-scale operations.
5. Safer for Miners
Without the need for dangerous chemicals or complex machinery, direct smelting is a safer option for miners. This method reduces the risk of exposure to toxic substances and accidents, improving the overall safety of mining operations.
Limitations of Direct Smelting
While direct smelting has many advantages, it also has some limitations:
- Requires Skilled Labor: Although the process is simple, it still requires some level of skill and knowledge to perform correctly. Miners need to know how to properly add flux, control the temperature, and pour the molten gold safely.
- Small-Scale Only: Direct smelting is most suitable for small-scale operations. Large-scale mining companies typically use more advanced methods such as the cyanide process or carbon-in-leach (CIL) for higher gold production.
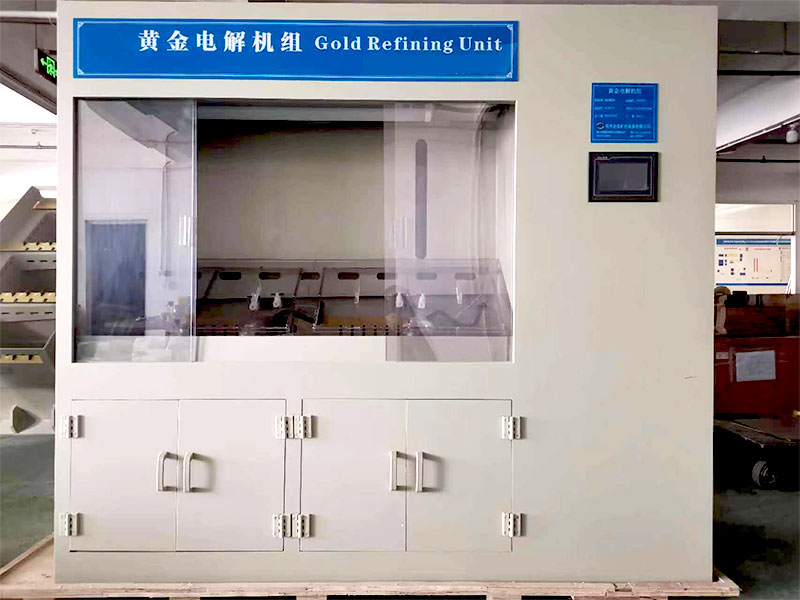
- Impurities in Gold: The gold produced through direct smelting may still contain impurities, requiring further refining for high-purity applications.
Direct smelting of gold is a valuable alternative to traditional gold recovery methods, especially for artisanal and small-scale miners. The process is simple, cost-effective, and mercury-free, offering a safer and more environmentally friendly option. While it may not be suitable for large-scale mining operations, direct smelting remains a reliable method for recovering gold from concentrates and ore. By using this technique, miners can achieve high gold recovery rates while reducing their environmental impact and improving the safety of their operations.