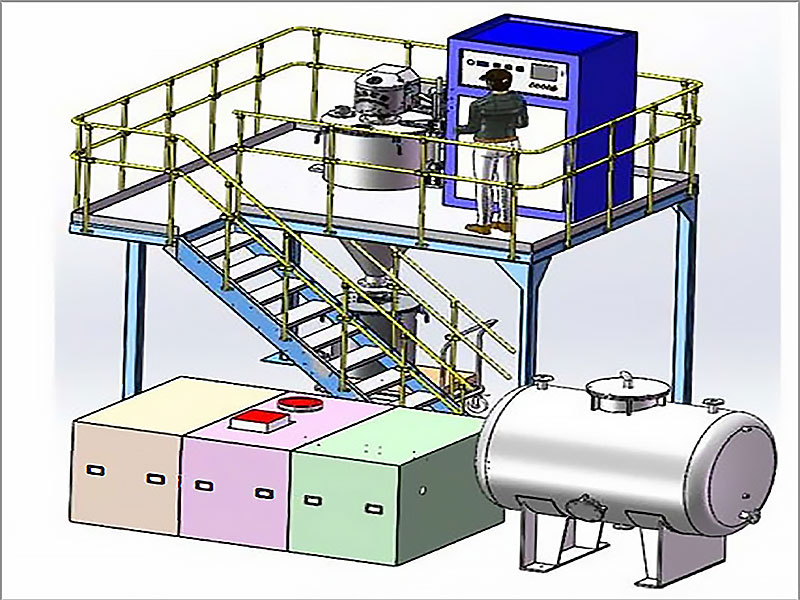
gold purification by electrolysis



Gold Purification by Electrolysis A Comprehensive Guide
Gold, one of the most valuable and sought-after metals, has been refined using various techniques for centuries. Among these methods, gold purification by electrolysis stands out for its ability to achieve high levels of purity with precision. This modern technique is widely used in the precious metals industry, providing a reliable way to purify gold efficiently. In this article, we will explore the process of electrolysis, its advantages, and its applications in the gold industry.
Understanding Gold Purification by Electrolysis
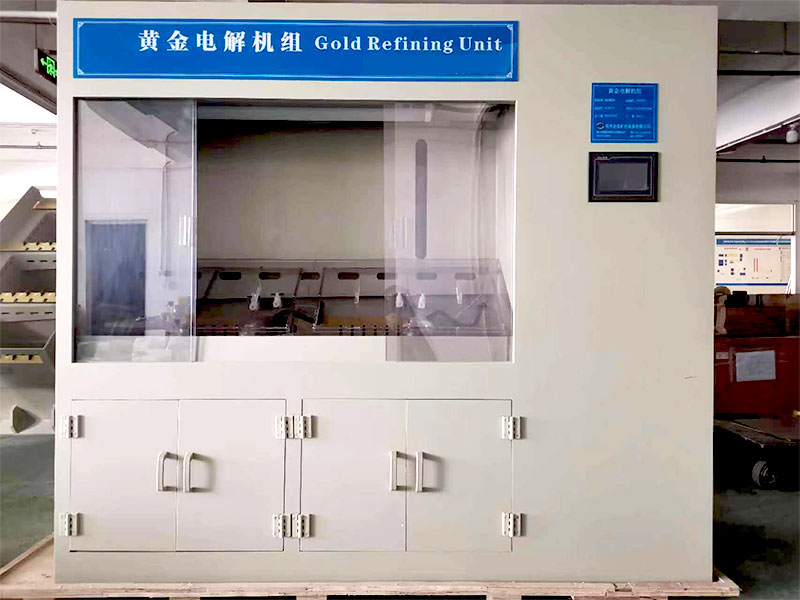
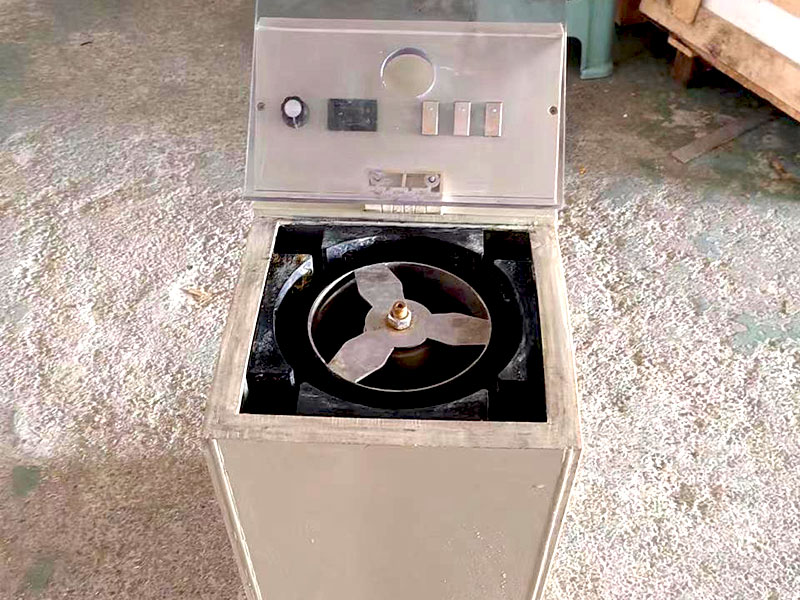
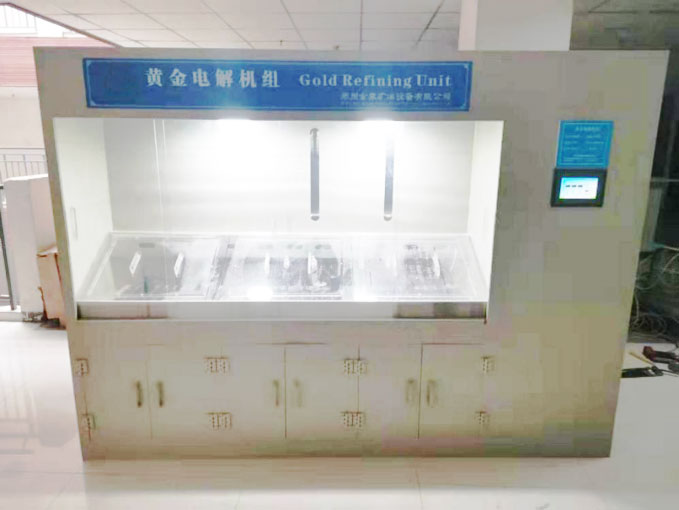
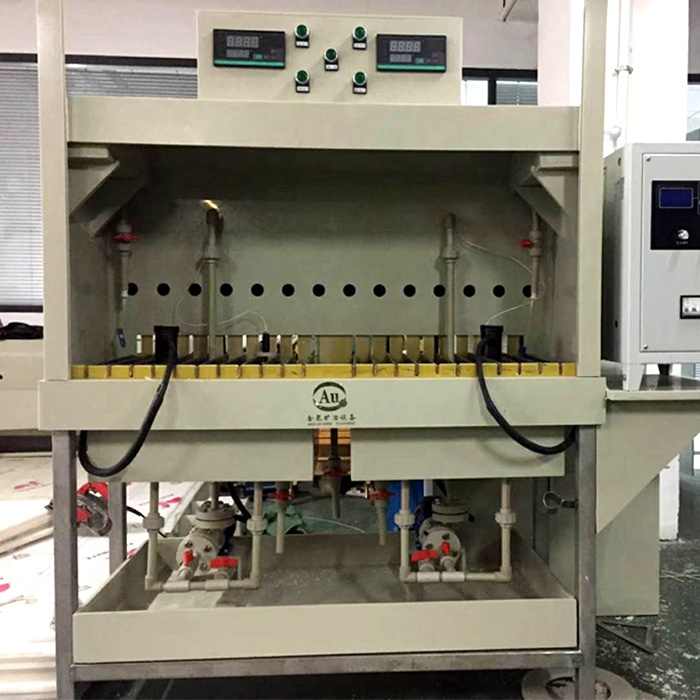
Electrolysis is a chemical process that uses an electric current to drive a non-spontaneous reaction. When applied to gold purification, it involves the use of an electrolytic cell where impure gold is dissolved into a solution and then deposited as pure gold on an electrode. This method is known for producing gold with a purity level of up to 99.99%, making it one of the most effective techniques available.
The key elements of the process include an electrolyte solution, a cathode, and an anode. The impure gold serves as the anode, while pure gold is deposited on the cathode. The electrolyte solution, typically a mixture of gold chloride or gold cyanide, allows the transfer of ions during the electrochemical reaction.
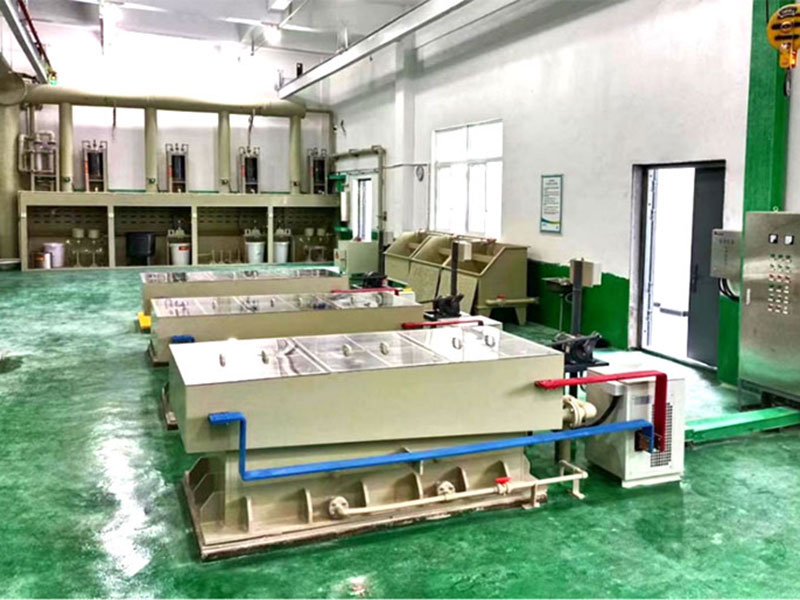
The Process of Gold Purification by Electrolysis
The electrolysis process for purifying gold involves several steps, each critical to achieving the desired purity. Here’s a breakdown of how the process works:
Dissolving Impure Gold
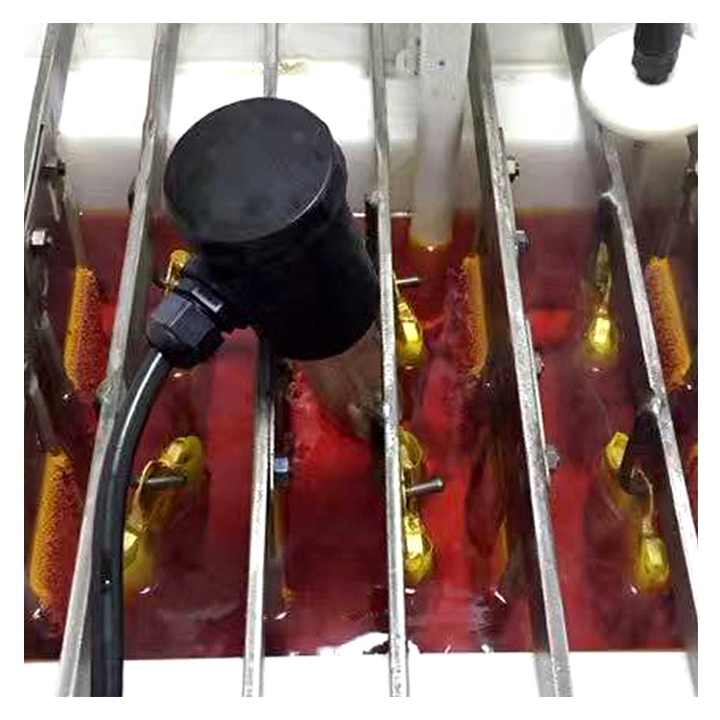
The first step in gold purification by electrolysis is to dissolve the impure gold in a suitable electrolyte solution. This solution usually contains gold chloride (AuCl₄⁻) or gold cyanide (Au(CN)₂⁻), depending on the specific method used. The impure gold, acting as the anode, is submerged in the solution and begins to dissolve as the electrochemical reaction progresses.
Ion Transfer
As the gold dissolves, gold ions (Au³⁺ or Au⁺) are released into the electrolyte solution. These ions then migrate toward the cathode, which is a thin sheet of pure gold or another conductive material. At the cathode, the gold ions are reduced and deposit as solid, pure gold.
Removing Impurities
During the electrolysis process, non-gold impurities either remain in the electrolyte solution or collect as a sludge at the bottom of the electrolytic cell. These impurities, which may include metals like copper, silver, and zinc, are separated from the pure gold as the reaction progresses. This ensures that the gold deposited on the cathode is of the highest purity.
Collecting the Pure Gold
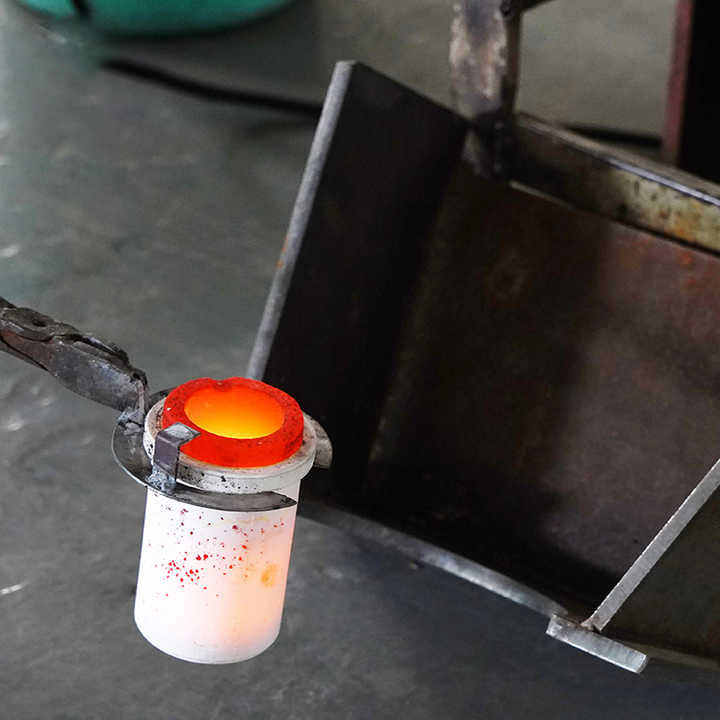
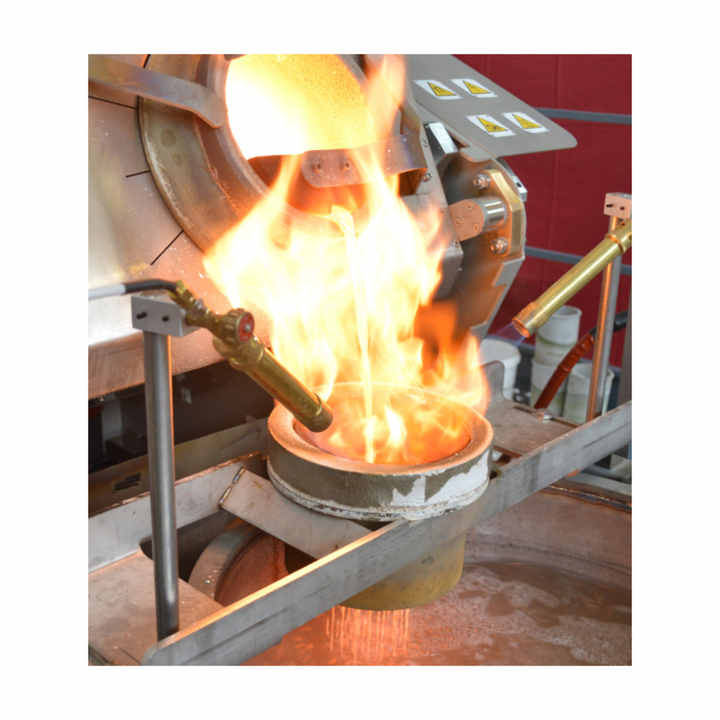
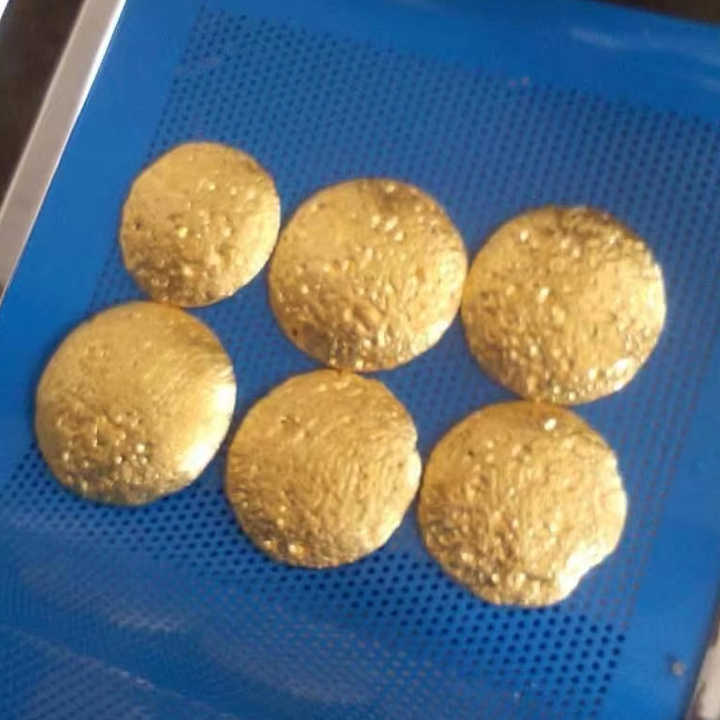
Once the electrolysis process is complete, the gold deposited on the cathode is carefully removed, often in the form of thin sheets or small granules. This gold is then melted and cast into bars, ingots, or other forms as required. The result is highly purified gold, suitable for various applications in jewelry, electronics, and other industries.
Advantages of Gold Purification by Electrolysis
Gold purification by electrolysis offers several advantages over traditional refining methods. These benefits include:
High Purity Levels
One of the most significant advantages of electrolysis is the ability to achieve extremely high purity levels, often up to 99.99%. This level of purity is essential for industries such as electronics, where even trace amounts of impurities can affect performance.
Efficiency
The electrolysis process is highly efficient, allowing large quantities of gold to be refined in a relatively short amount of time. This efficiency makes it a cost-effective option for gold producers looking to purify their output on an industrial scale.
Environmentally Friendly
Compared to other gold purification methods, such as smelting, electrolysis is less harmful to the environment. The use of chemicals is more controlled, and emissions are significantly reduced, making it a more sustainable option for gold refining.
Precision
Electrolysis allows for precise control over the purification process. By adjusting variables such as the voltage and concentration of the electrolyte solution, refineries can fine-tune the process to achieve the desired purity levels without excessive waste.
Applications of Gold Purification by Electrolysis
Gold purification by electrolysis is used in a wide range of industries, particularly those that require high-purity gold for manufacturing or investment purposes. Some of the most common applications include:
Jewelry Making
In the jewelry industry, the demand for high-purity gold is constant. Electrolytic purification ensures that the gold used in fine jewelry is free from impurities, providing a bright, lustrous finish that enhances the aesthetic appeal and value of the pieces.
Electronics Manufacturing
Gold is an excellent conductor of electricity, which makes it invaluable in the electronics industry. However, even small amounts of impurities can reduce its effectiveness. Electrolytic refining ensures that the gold used in electronics, such as connectors and circuit boards, is of the highest quality.
Coinage and Bullion
Many gold coins and bullion bars are made from gold purified through electrolysis. The process ensures that these investment-grade products meet the stringent purity standards required by governments and financial institutions.
Dentistry and Medical Devices
Gold’s biocompatibility makes it a popular material for dental work and medical devices. Electrolytic refining ensures that the gold used in these applications is free from contaminants, reducing the risk of adverse reactions and ensuring durability.
Gold purification by electrolysis is a highly effective method for refining gold to achieve maximum purity. Through a controlled electrochemical process, impurities are removed, and pure gold is deposited, making it suitable for various high-demand applications. With its advantages of high efficiency, precision, and environmental friendliness, electrolysis continues to be a leading technique in the gold refining industry. As the demand for pure gold remains strong across industries, the role of electrolysis in refining will only continue to grow.