Gold Refining With Mercury And Sulfuric Acid
Gold Refining With Mercury And Sulfuric Acid: An Overview
Gold refining processes have evolved significantly over time to meet environmental and efficiency standards. One method that has been used historically, although controversial due to its environmental impact, involves the combination of mercury and sulfuric acid. This process, while not commonly practiced today due to stringent regulations, offers insights into how gold can be extracted and refined. FRT Machinery, a leader in providing innovative solutions for the mining industry, explores the complexities and concerns surrounding this method.
Understanding the Role of Mercury in Gold Refining
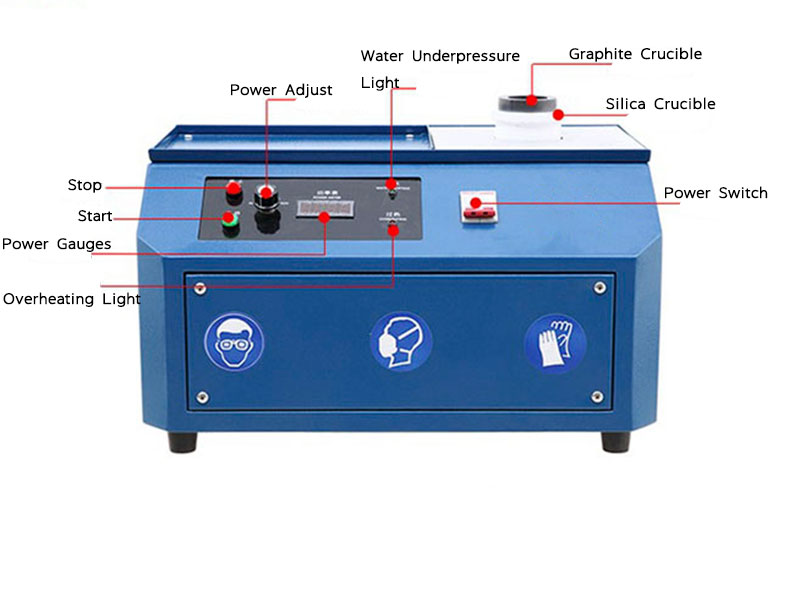
Mercury amalgamation is a technique that has been utilized for centuries to extract gold from its ores. When gold particles come into contact with mercury, they form an amalgam—a solid mixture that allows for easier separation from non-metallic materials. In the context of refining, mercury serves as a binding agent, effectively capturing free gold and other precious metals. However, the use of mercury poses significant health and environmental risks, which have led to its phased-out usage in many parts of the world.
Sulfuric Acid in Gold Refining Processes
Sulfuric acid plays a dual role in gold refining when combined with mercury. Firstly, it helps in breaking down certain compounds within the ore, making it easier for mercury to interact with the gold content. Secondly, sulfuric acid aids in the cleaning process post-amalgamation, ensuring that the extracted gold is free from impurities. Despite these benefits, handling sulfuric acid requires extreme caution due to its corrosive nature and potential to cause severe burns upon contact.
Safety Concerns in Using Mercury and Sulfuric Acid

The primary concern associated with using mercury and sulfuric acid in gold refining is the potential harm to both human health and the environment. Mercury vapor is toxic, leading to neurological damage if inhaled. Similarly, improper disposal of mercury-contaminated waste can lead to water pollution, affecting aquatic life and local communities. Sulfuric acid, being highly corrosive, demands careful handling to prevent accidents such as spills or splashes, which could result in serious injuries.
Environmental Impact of Mercury and Sulfuric Acid in Refining
The environmental toll of employing mercury and sulfuric acid in gold refining cannot be overstated. Mercury contamination can persist in ecosystems for decades, bioaccumulating in food chains and posing long-term risks to wildlife and human populations. Moreover, the acidic runoff from refining operations can alter soil pH levels, impacting plant growth and biodiversity. Regulations like the Minamata Convention on Mercury have been implemented globally to reduce mercury emissions and promote safer alternatives.
Modern Alternatives to Mercury and Sulfuric Acid Refining
Recognizing the drawbacks of traditional methods, FRT Machinery advocates for and develops advanced technologies that minimize reliance on hazardous chemicals. Techniques such as cyanidation, although still involving chemicals, offer more controlled environments for gold extraction. Additionally, physical separation methods like gravity concentration and magnetic separation are gaining traction as environmentally friendly alternatives. These innovations aim to balance economic viability with sustainability, ensuring that future generations inherit a healthier planet.

The Future of Gold Refining Without Mercury and Sulfuric Acid


As global awareness grows regarding the adverse effects of mercury and sulfuric acid on the environment and public health, there is a clear shift towards cleaner, more sustainable practices in the mining industry. FRT Machinery continues to invest in research and development to bring forth new solutions that not only enhance efficiency but also prioritize safety and environmental stewardship. By working together, we can pave the way for a greener future in gold refining, one that respects our planet’s limits and promotes responsible resource management.
Through ongoing innovation and adherence to stringent safety protocols, the industry moves closer to achieving a balance between economic prosperity and ecological responsibility.