Gold Smelting Chemistry
Understanding the Fundamentals of Gold Smelting Chemistry
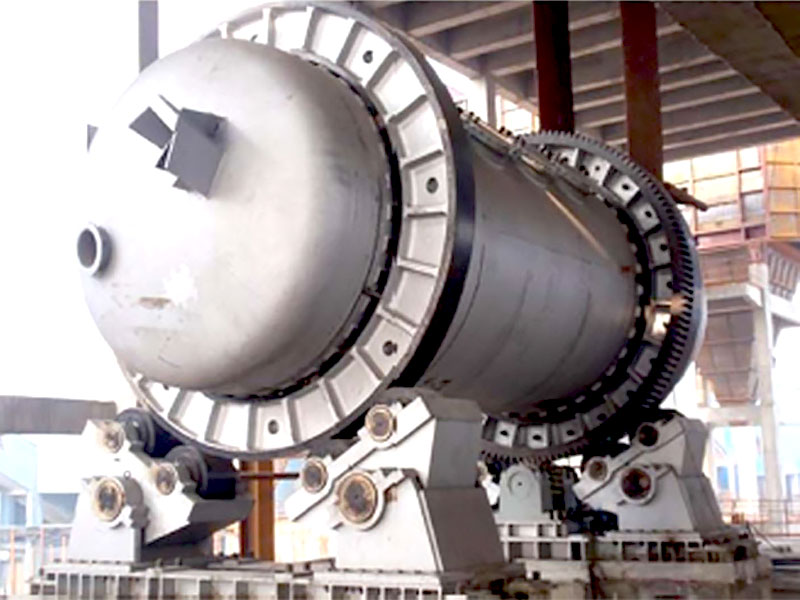
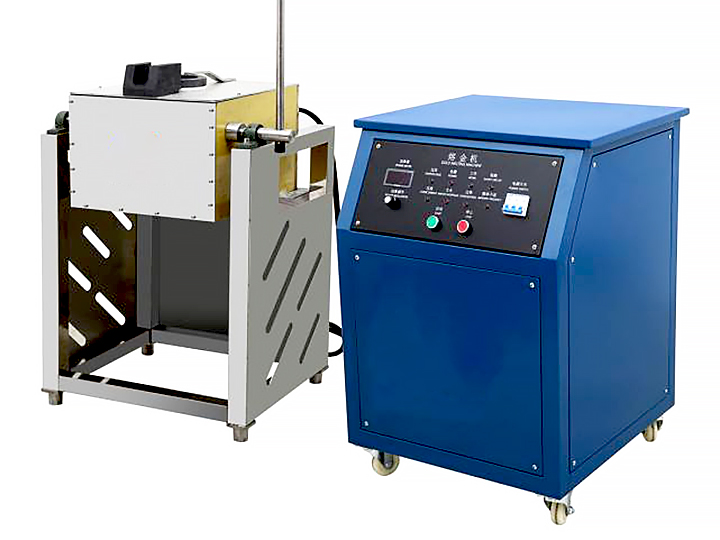
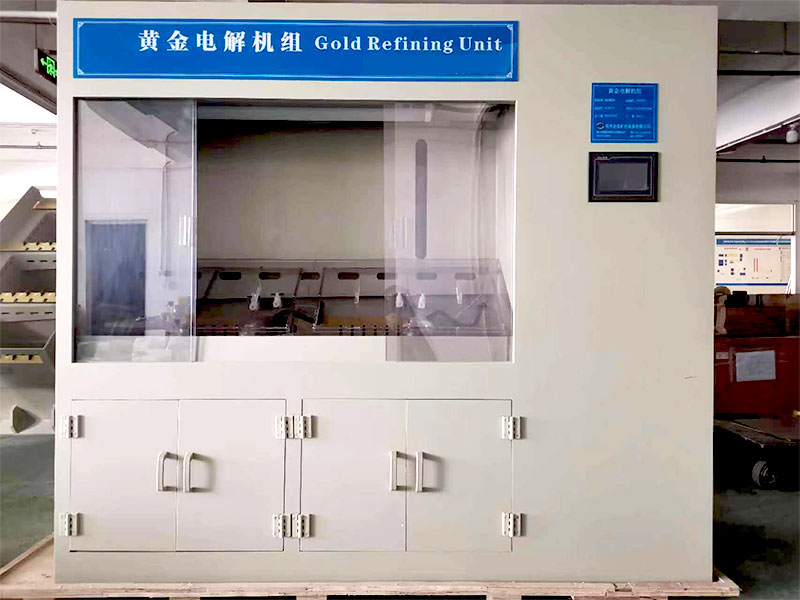
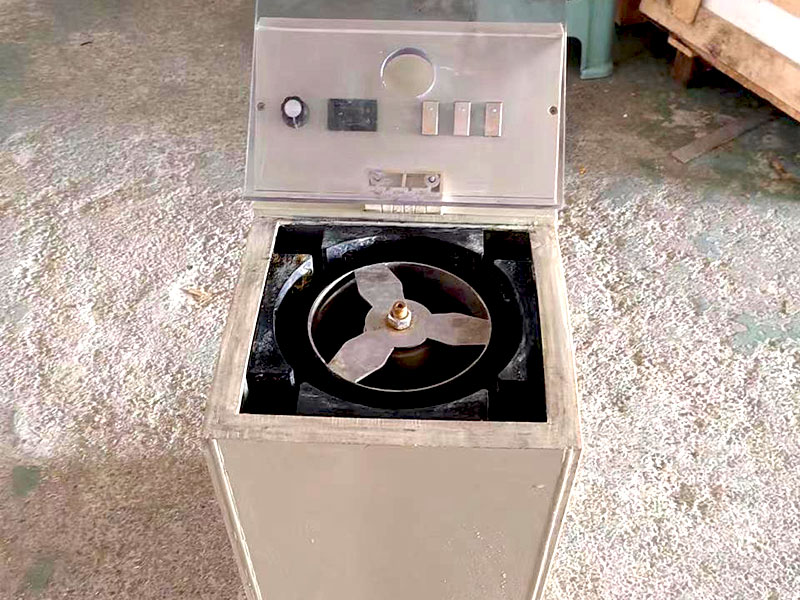
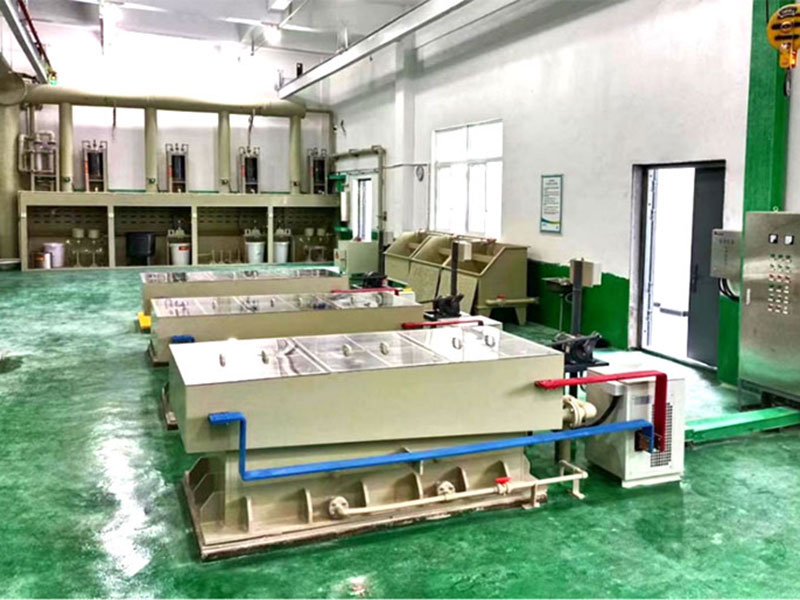
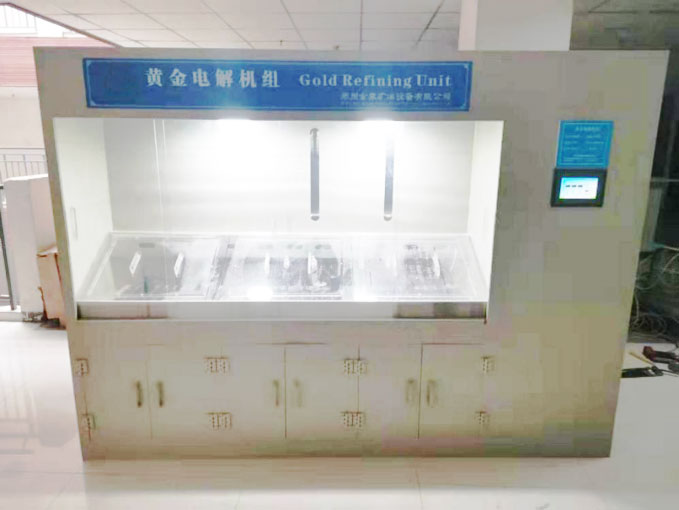
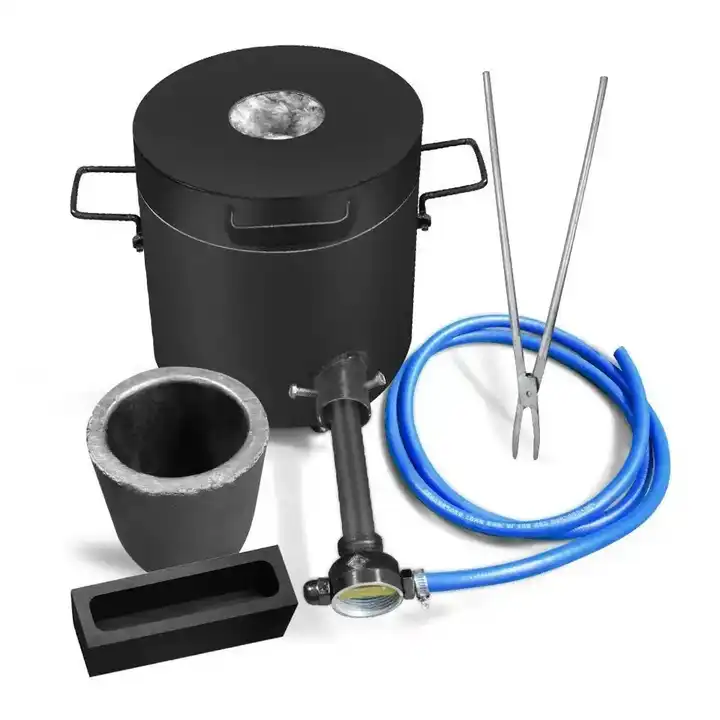
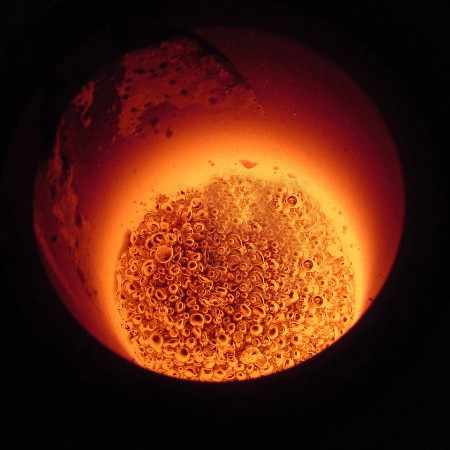
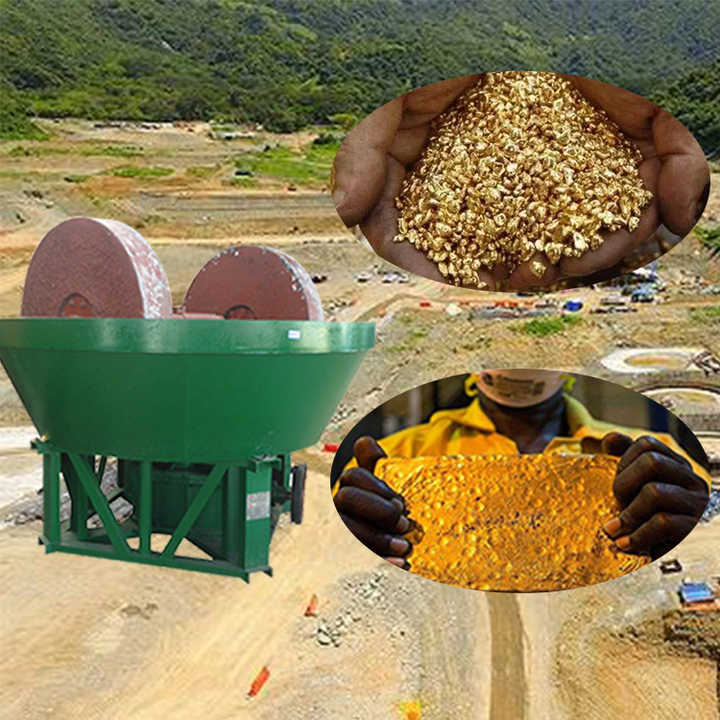
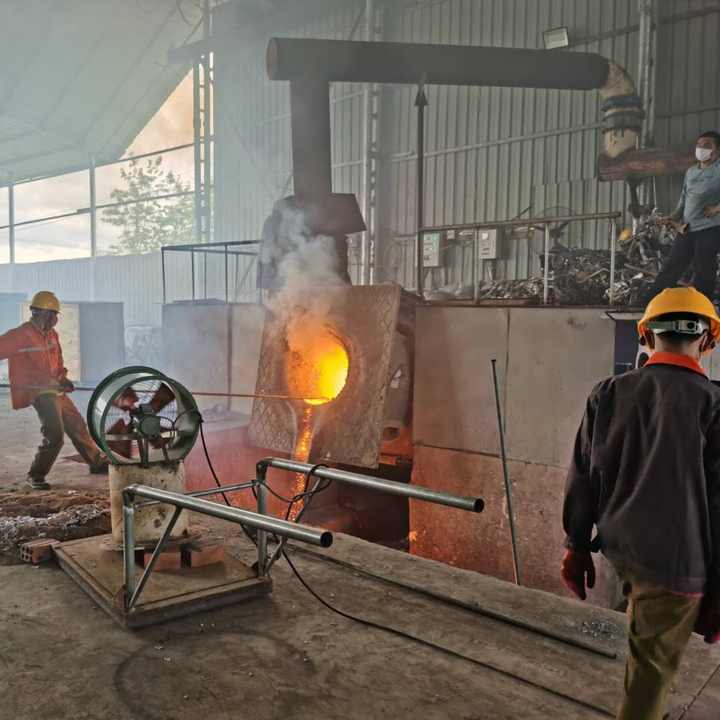
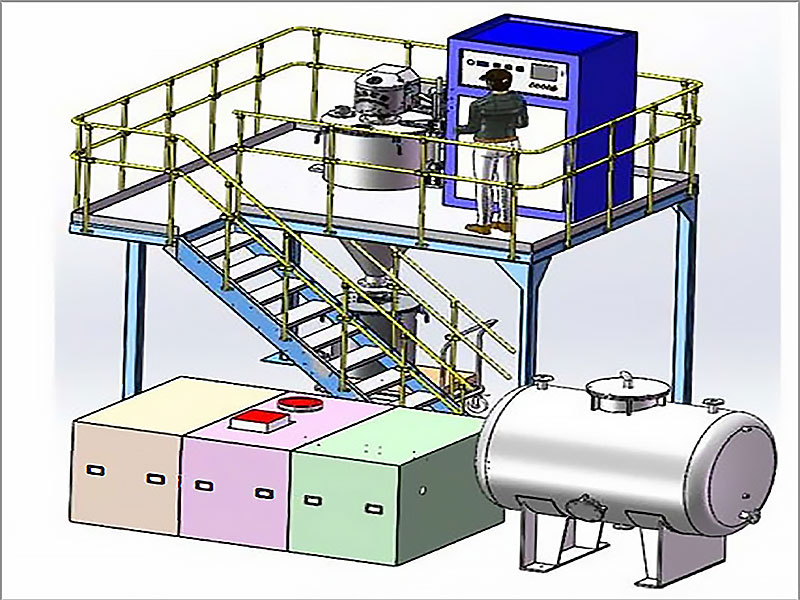
Gold smelting is a time-honored technique for extracting gold from its raw form. It involves the application of heat to ore or concentrate, often in the presence of fluxes and reducing agents, to melt out and separate gold from other minerals. This process requires a deep understanding of the chemical interactions involved. As experts in metallurgical processes, FRT Machinery has developed innovative solutions that enhance efficiency and sustainability in gold smelting. Here, we delve into the chemistry behind this essential process, exploring how it transforms raw materials into valuable gold.
The Role of Fluxes in Gold Smelting Chemistry
Fluxes play a critical role in gold smelting chemistry by lowering the melting point of non-metallic impurities, allowing them to be separated from the molten metal. Commonly used fluxes include silica (SiO2), lime (CaO), and soda ash (Na2CO3). These substances react with the gangue materials present in the ore, forming a slag that floats on top of the molten gold. By carefully controlling the composition and temperature of the smelting process, FRT Machinery’s systems ensure maximum recovery of gold while minimizing environmental impact.

Reducing Agents in Gold Smelting Chemistry
The addition of reducing agents is another key aspect of gold smelting chemistry. These substances help convert gold compounds back into pure metallic gold. Common reducing agents include coke, charcoal, and carbon monoxide. During the smelting process, these materials react with oxygen, preventing it from binding with gold and other valuable metals. FRT Machinery designs its furnaces to optimize the use of these agents, ensuring complete reduction and efficient smelting operations.
Temperature Control in Gold Smelting Chemistry

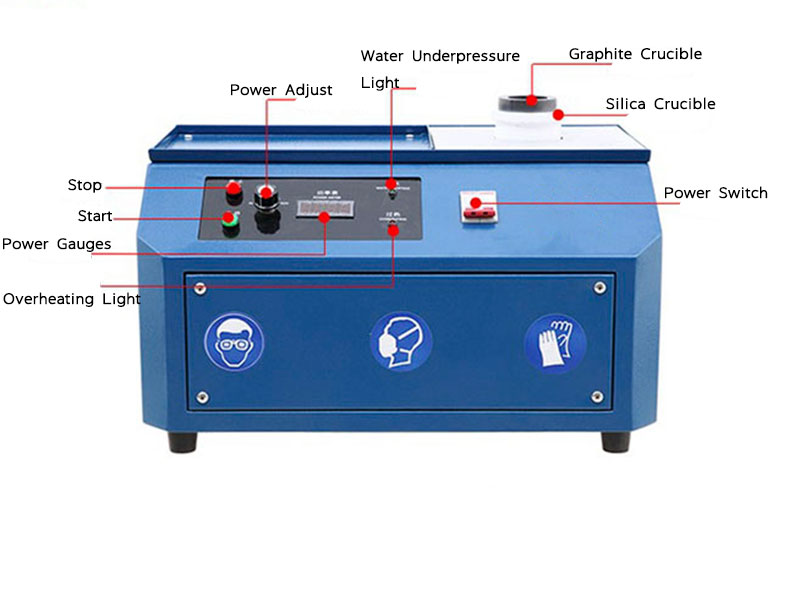
Temperature control is crucial in gold smelting chemistry, as it directly affects the efficiency of the separation process. Too low a temperature can result in incomplete melting and poor separation of gold from impurities; too high a temperature can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and potential damage to the smelting equipment. FRT Machinery’s advanced temperature management systems maintain optimal conditions throughout the smelting cycle, maximizing gold yield and operational safety.
Environmental Considerations in Gold Smelting Chemistry
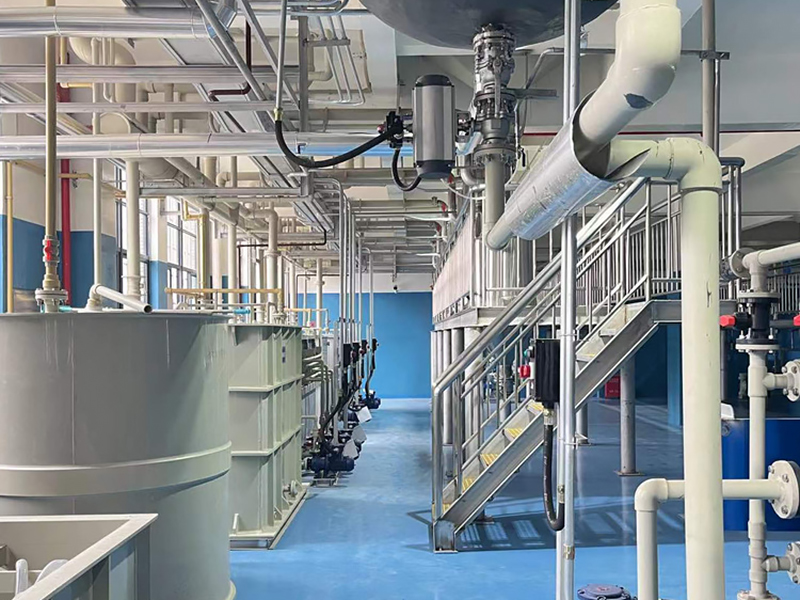
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in gold smelting chemistry. Traditional smelting methods can release harmful gases and particulates into the atmosphere. To address these concerns, FRT Machinery incorporates state-of-the-art filtration and emission control technologies into its smelting systems. These innovations not only reduce the environmental footprint of gold production but also comply with stringent international standards for air quality and pollution control.
Innovations in Gold Smelting Chemistry
Advancements in gold smelting chemistry continue to drive innovation within the industry. New techniques such as microwave-assisted smelting and the use of biologically derived reagents offer promising alternatives to conventional methods. FRT Machinery invests heavily in research and development to explore these emerging technologies, aiming to set new benchmarks in efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness for gold smelting operations worldwide.
By focusing on these core aspects of gold smelting chemistry, FRT Machinery supports the global gold industry in achieving higher yields, lower operating costs, and a reduced environmental impact. Through continuous innovation and a commitment to excellence, FRT Machinery remains at the forefront of advancements in gold smelting technology.