junk silver smelting

Junk Silver Smelting: A Profitable Endeavor
Junk silver smelting has gained popularity among enthusiasts and investors looking to reclaim value from old silver coins and other silver items. This process involves melting down junk silver to extract its precious metal content, often leading to significant financial returns. In this article, we will explore what junk silver is, the smelting process, and the potential profitability of this venture.

Understanding Junk Silver
Junk silver refers to coins that contain a significant amount of silver but are no longer in circulation. Typically, these are U.S. coins minted before 1965, such as dimes, quarters, and half dollars, which contain 90% silver. Despite their diminished numismatic value, junk silver is sought after for its metal content, making it a popular choice for smelting.
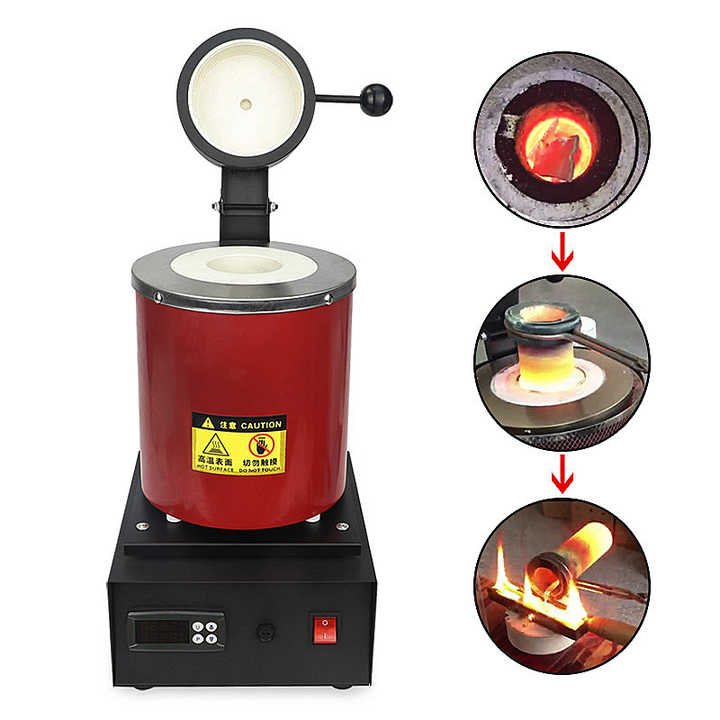

The Smelting Process
The smelting of junk silver involves several key steps:
Collection and Preparation
The first step in junk silver smelting is gathering the coins or silver items. It’s essential to sort them by purity, as not all silver items have the same silver content. Once collected, the coins should be cleaned to remove any contaminants or dirt, which can interfere with the smelting process.
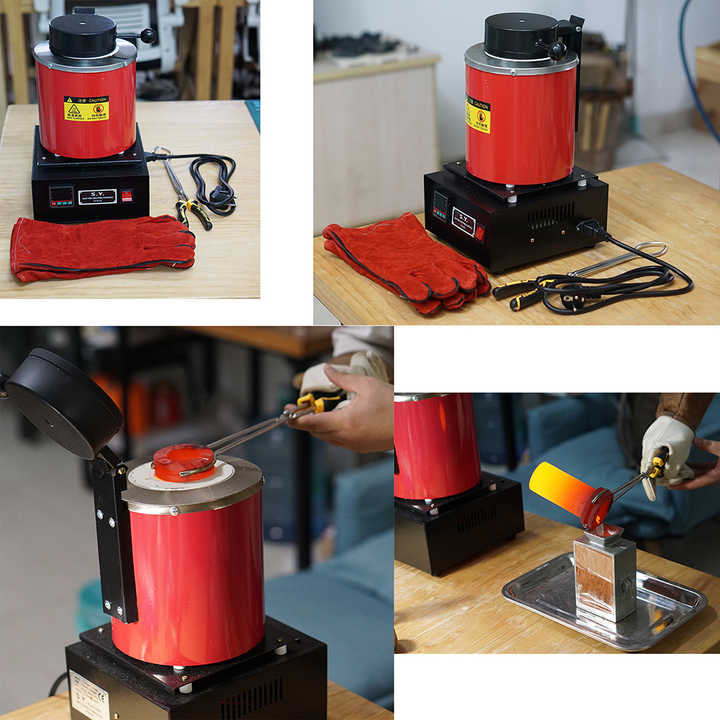
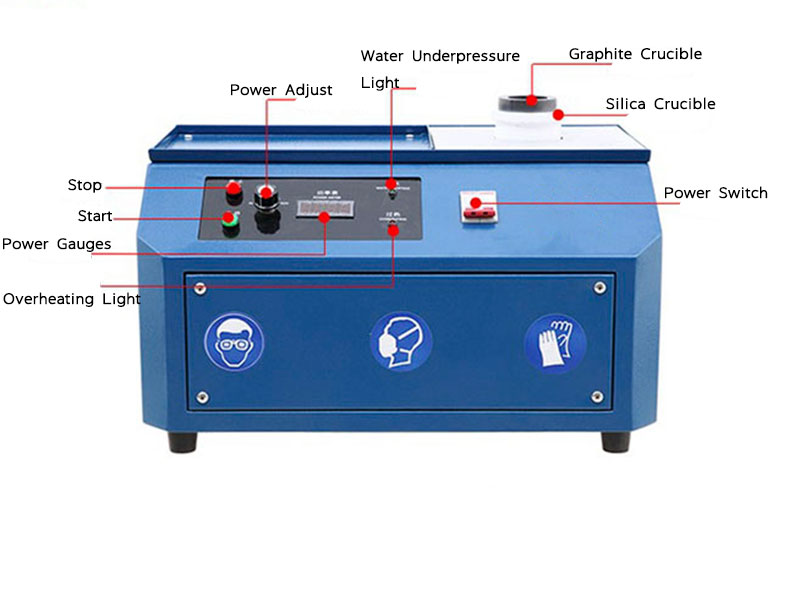
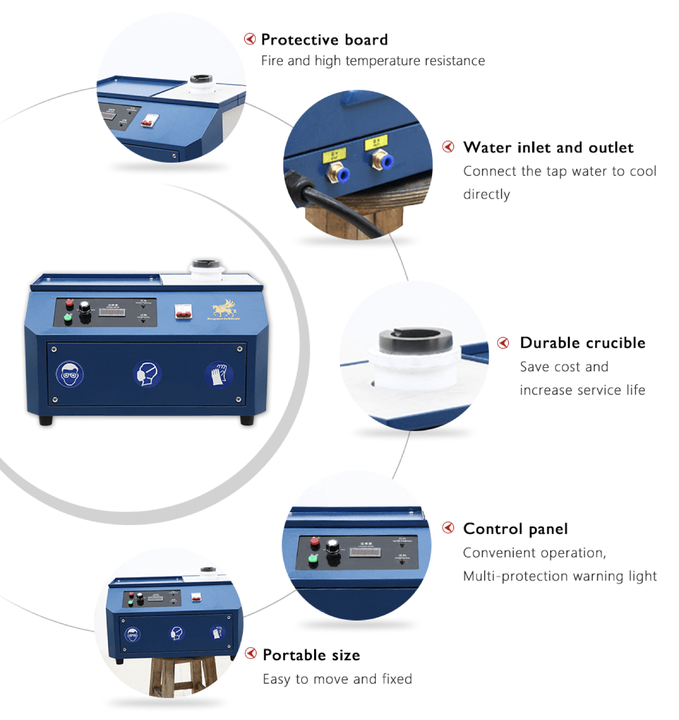
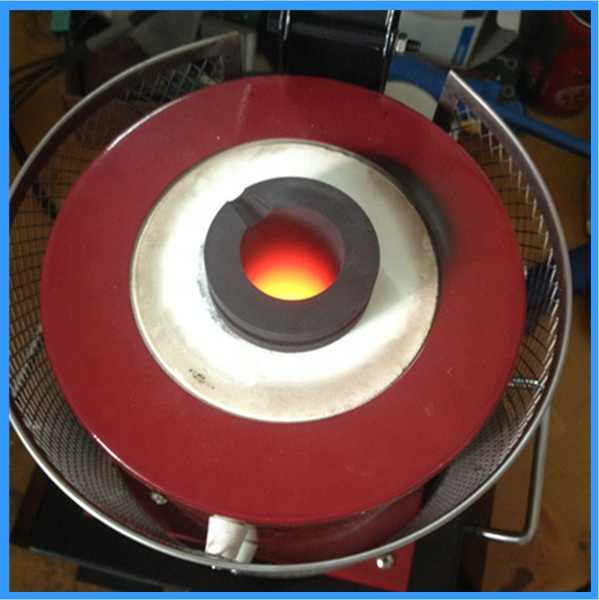
Melting
After preparation, the junk silver is melted in a crucible. The melting point for silver is around 1,763°F (961.8°C), so a high-temperature furnace is necessary. Flux, such as borax, can be added to help separate impurities from the molten silver. This step ensures a purer end product.
Pouring and Solidification
Once the silver is fully melted and impurities have been removed, it is poured into molds to solidify. The solidified silver can then be further processed or sold.
Profitability Factors
Several factors can influence the profitability of junk silver smelting:
Current Silver Prices
The price of silver fluctuates in the market, and higher prices can lead to greater profits from smelting. Keeping an eye on market trends can help smelters decide the optimal time to sell their silver.
Quantity and Purity
The amount of junk silver and its purity also play a significant role in profitability. The more silver one has, the greater the potential returns. Additionally, ensuring that the coins are primarily made of silver (such as 90% silver coins) will maximize the yield during smelting.
Costs of Smelting
While smelting can be profitable, associated costs must be considered. This includes equipment, fuel, and time invested in the smelting process. For small-scale operations, these costs can sometimes outweigh potential profits.
Alternatives to Smelting
For those who find smelting to be less profitable, there are alternative options:
- Selling Coins As Is: If the coins hold numismatic value, selling them in their current condition can yield higher returns than smelting.
- Local Refiners: Many local refining services will purchase junk silver and handle the smelting process for a fee. This option saves time and effort, allowing individuals to benefit from their silver without the hassle of melting it down themselves.
Junk silver smelting can be a rewarding venture for those looking to capitalize on their old silver coins. With the right preparation, understanding of the smelting process, and market awareness, individuals can potentially turn a profit from their junk silver. However, it’s essential to weigh the associated costs and consider alternative options to ensure the best financial outcome. Whether smelting or selling, there’s value to be found in these historical silver pieces, making them an attractive option for investors and hobbyists alike.