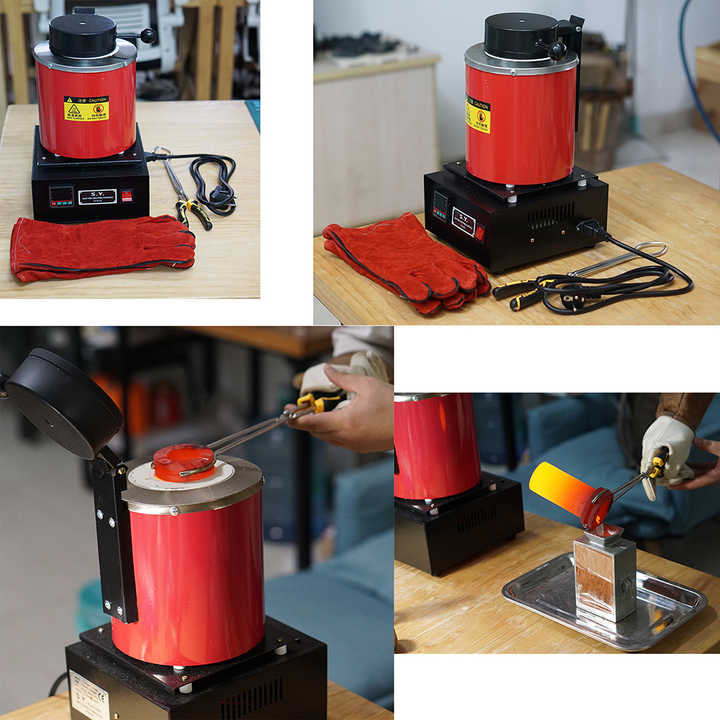
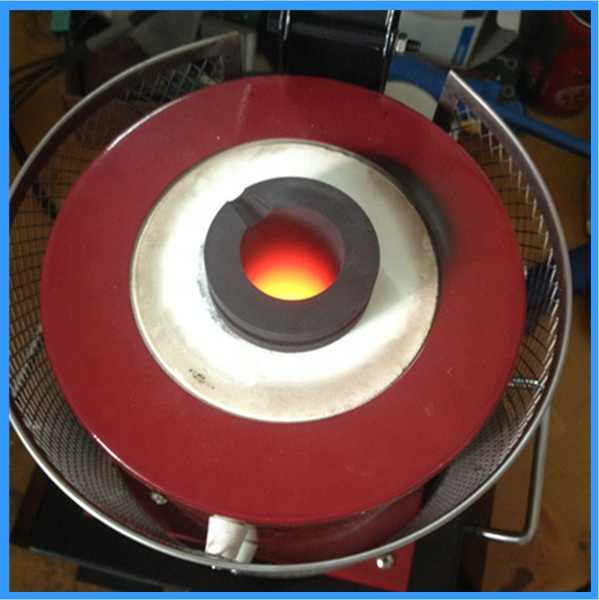
methods of smelting for silver and lead
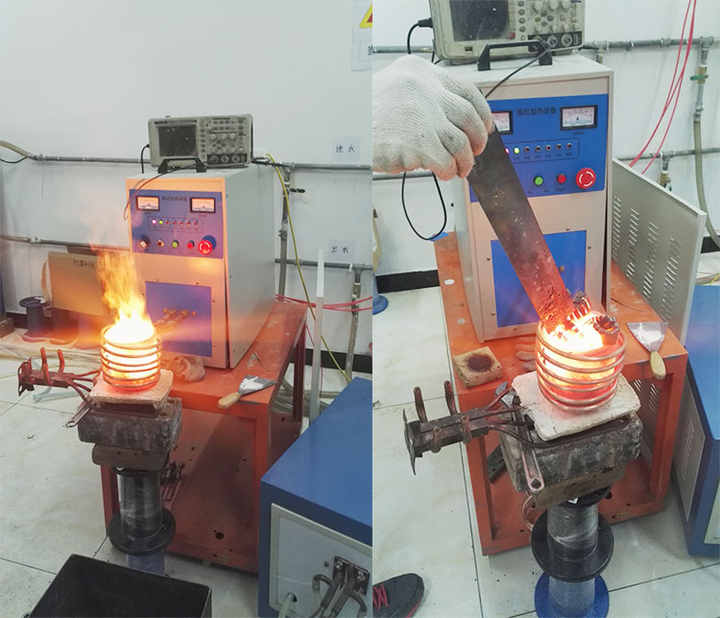


Smelting is a critical process in the extraction of metals from their ores, particularly for precious metals like silver and common metals such as lead. This article explores various methods of smelting for silver and lead, highlighting their processes, advantages, and considerations.
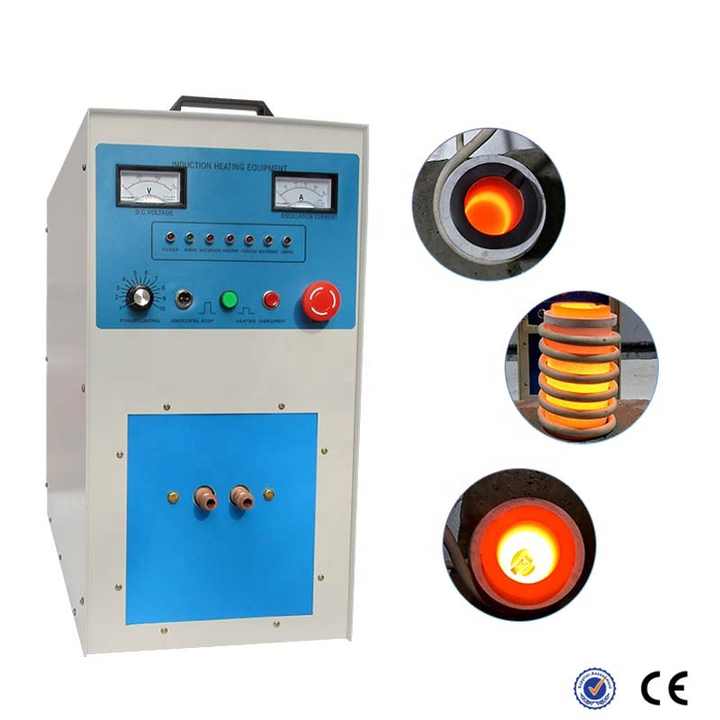


Understanding Smelting
Smelting is a pyrometallurgical process that involves heating ores to extract metals. It typically requires a source of heat and a reducing agent, such as carbon, to facilitate the conversion of metal oxides into pure metals. The methods used for smelting silver and lead can differ based on the ore’s composition and the desired purity.
Methods of Smelting for Silver
Cupellation
Cupellation is one of the oldest and most effective methods for refining silver. This process involves heating silver ore in a furnace along with a flux (such as lead oxide) to separate impurities. The steps are as follows:
- Crushing and Grinding: The ore is crushed and ground into a fine powder to increase the surface area for reaction.
- Mixing with Flux: The powdered ore is mixed with a flux and placed in a crucible.
- Heating: The mixture is heated in a furnace, causing the silver to melt and the impurities to form a slag.
- Separation: The molten silver is poured off, leaving behind the slag.
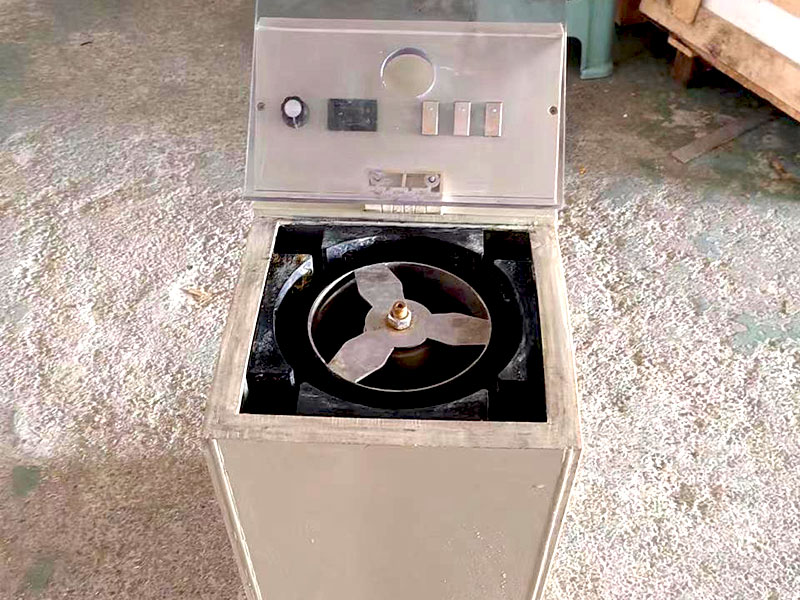
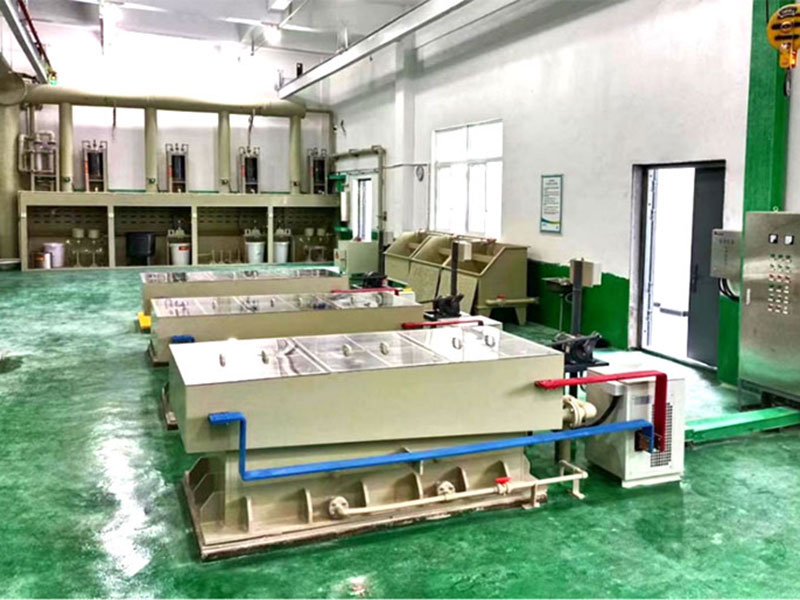
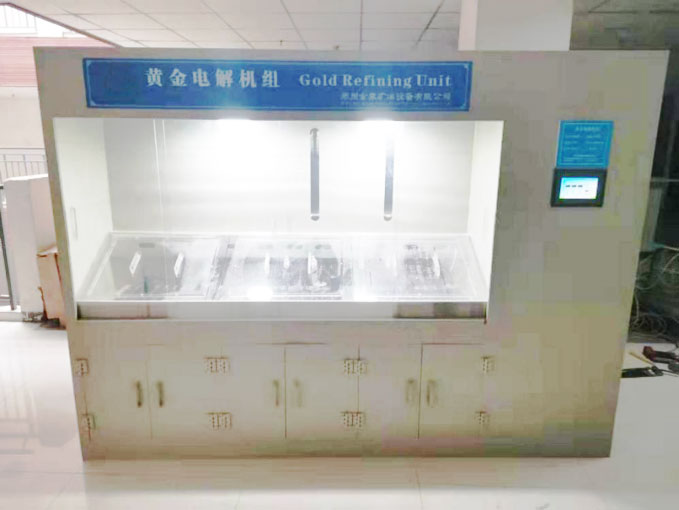
Electrolytic Refining
Electrolytic refining is a more modern technique used to achieve high purity levels. In this method:
- Preparation of an Electrolyte: A silver salt solution is prepared as the electrolyte.
- Electrolysis: An electric current is passed through the solution, causing silver ions to migrate to a cathode where they are deposited as pure silver.
- Recovery of Impurities: Impurities remain in the solution or settle at the bottom, allowing for high-purity silver extraction.
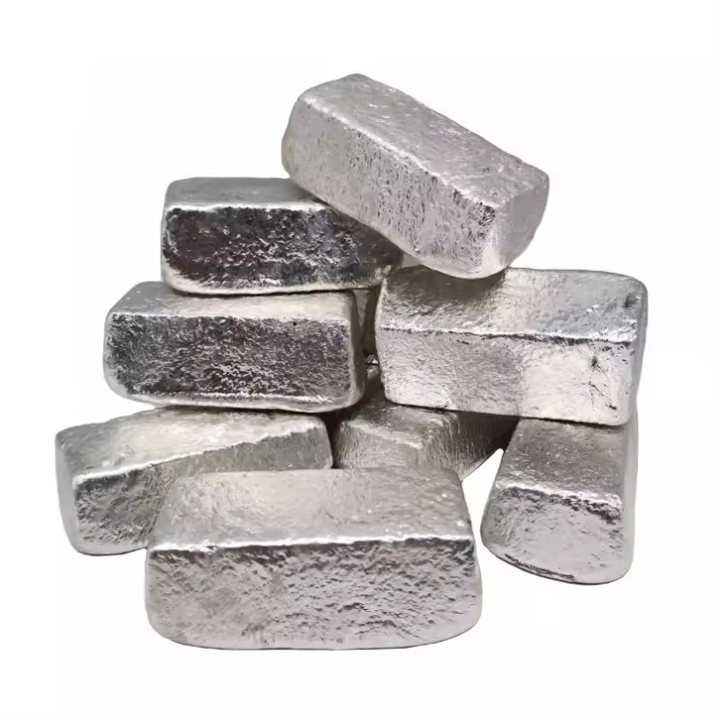


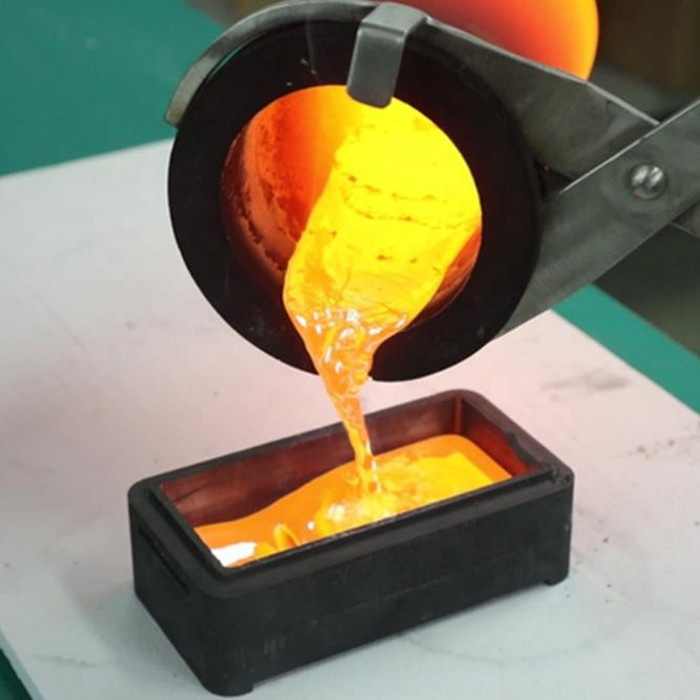
Methods of Smelting for Lead
Blast Furnace Smelting
Blast furnace smelting is a widely used method for extracting lead from its ores, particularly galena (PbS). The process involves:
- Concentration: The ore is concentrated through crushing and flotation to remove impurities.
- Charging the Furnace: Concentrated ore, coke, and flux are added to a blast furnace.
- Combustion: Air is blown into the furnace, igniting the coke and generating the high temperatures needed to melt lead.
- Collection of Lead: The molten lead sinks to the bottom of the furnace, where it can be tapped off, while slag forms on the surface.
Pyrometallurgical Process
This method combines roasting and smelting:
- Roasting: The lead ore is first roasted to convert lead sulfide to lead oxide.
- Smelting: The roasted ore is then smelted in a furnace with a reducing agent, typically carbon, to produce lead metal.
Comparison of Methods
- Efficiency: Cupellation and blast furnace methods are efficient for bulk processing, while electrolytic refining offers high purity.
- Cost: Traditional methods, such as cupellation, can be less expensive than modern electrolytic techniques but may require more labor and time.
- Environmental Impact: Modern methods, particularly electrolytic refining, tend to produce less waste and are more environmentally friendly compared to traditional smelting techniques.
The methods of smelting for silver and lead vary widely, reflecting the complexities of their ores and the desired purity of the final product. From traditional techniques like cupellation to modern methods such as electrolytic refining, each process has its unique advantages and considerations. Understanding these methods can help metalworkers choose the most appropriate technique for their specific needs, whether they are refining precious metals or extracting common ones.