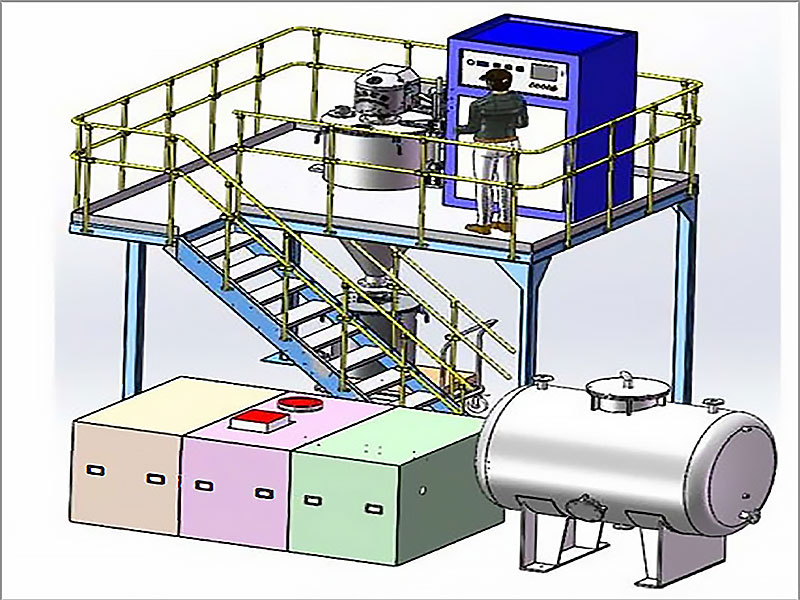
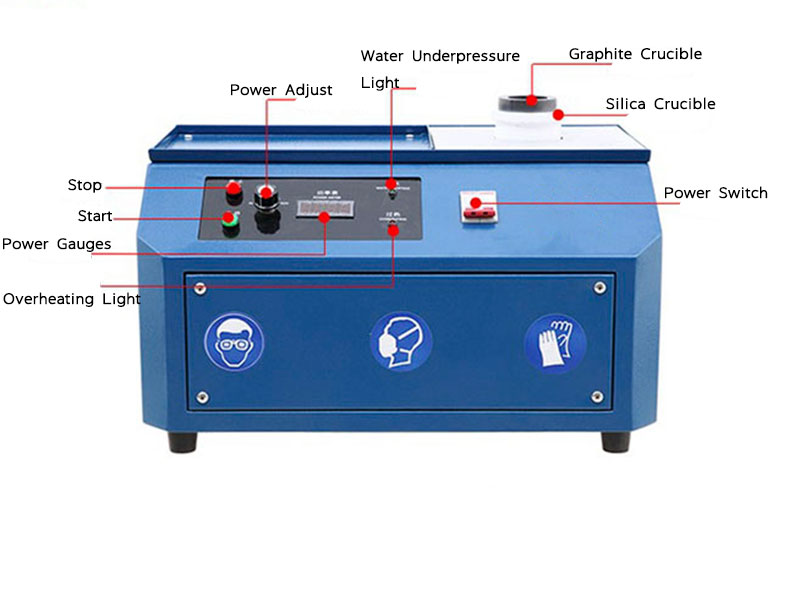
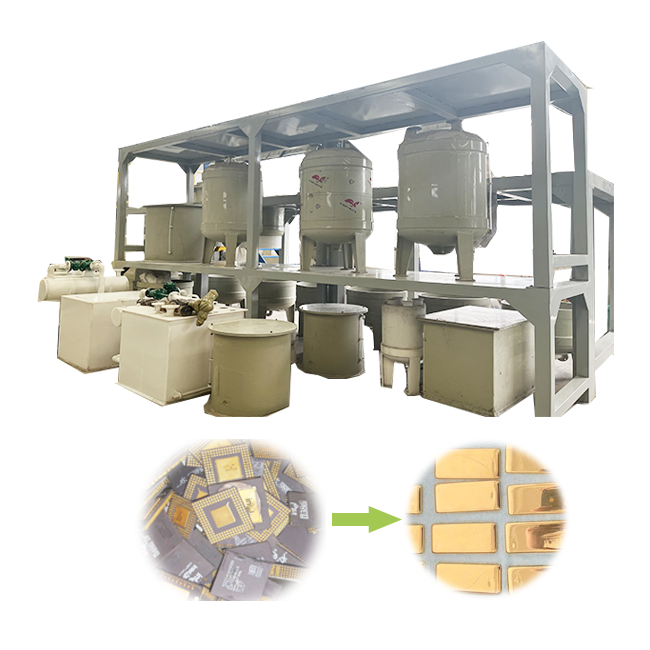
processing and refining gold
Processing and Refining Gold: Techniques, Steps, and Industry Insights
Processing and refining gold are critical operations that transform raw ore into pure gold, ready for use in a variety of applications. From extraction methods to the refinement of gold, the process involves several technical steps designed to maximize the yield and purity of the precious metal. This article explores the methods, stages, and industry perspectives on processing and refining gold. 

The Initial Stages of Processing and Refining Gold
The journey of processing and refining gold begins with the extraction of gold-bearing ore from the earth. The methods used in this stage can vary depending on the nature of the deposit and the economic considerations of the operation.
- Mining and Extraction:
- Open-Pit Mining: This method is used when gold deposits are located close to the surface. Large machines are used to remove the overburden and access the ore. The extracted ore is then transported to processing facilities for further refinement.
- Underground Mining: When gold deposits are located deeper underground, miners use tunnels and shafts to access the ore. This method is more labor-intensive and costly but is necessary for accessing rich deposits that are not reachable by surface mining.
- Placer Mining: This technique is used to extract gold from alluvial deposits in riverbeds and streams. Placer mining involves washing sediment to separate gold particles from sand, gravel, and other materials.
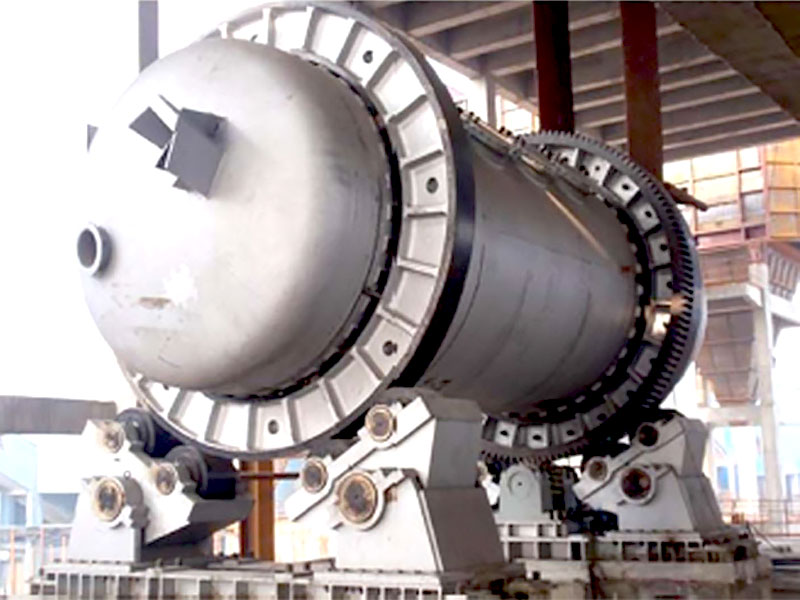
- Crushing and Grinding:
- Once the gold ore is extracted, it undergoes a series of crushing and grinding processes to reduce the size of the particles. This step is crucial as it increases the surface area of the ore, making it easier to extract the gold during the refining stages.
- Concentration:
- After the ore is crushed, concentration methods such as gravity separation or flotation are used to separate gold from other minerals. In gravity separation, gold is concentrated by taking advantage of its higher density compared to other materials. In flotation, chemicals are added to the crushed ore to make the gold particles adhere to bubbles and rise to the surface, where they can be skimmed off.



Advanced Techniques in Processing and Refining Gold
Processing and refining gold involves several advanced techniques that ensure the extraction of high-purity gold from the ore. These methods are carefully chosen based on the characteristics of the ore and the desired purity level of the final product.
- Cyanidation Process:
- Leaching: One of the most widely used methods in processing and refining gold is cyanidation, where a cyanide solution is used to dissolve gold from the ore. The leaching process involves mixing the crushed ore with a dilute cyanide solution, which selectively dissolves the gold. This solution is then separated from the ore to recover the dissolved gold.
- Carbon-in-Pulp (CIP) and Carbon-in-Leach (CIL): These are two variations of the cyanidation process. In the CIP method, activated carbon is added to the leached solution, where it adsorbs the gold. The gold-laden carbon is then separated, and the gold is recovered through further refining. In the CIL process, the carbon is added directly to the leaching tanks, allowing for simultaneous leaching and adsorption.
- Heap Leaching:
- Heap leaching is a cost-effective method used in processing and refining gold from low-grade ores. The ore is piled up on a large pad, and a cyanide solution is sprayed over the heap. The solution percolates through the heap, dissolving the gold, which is then collected at the bottom and processed to extract the gold.
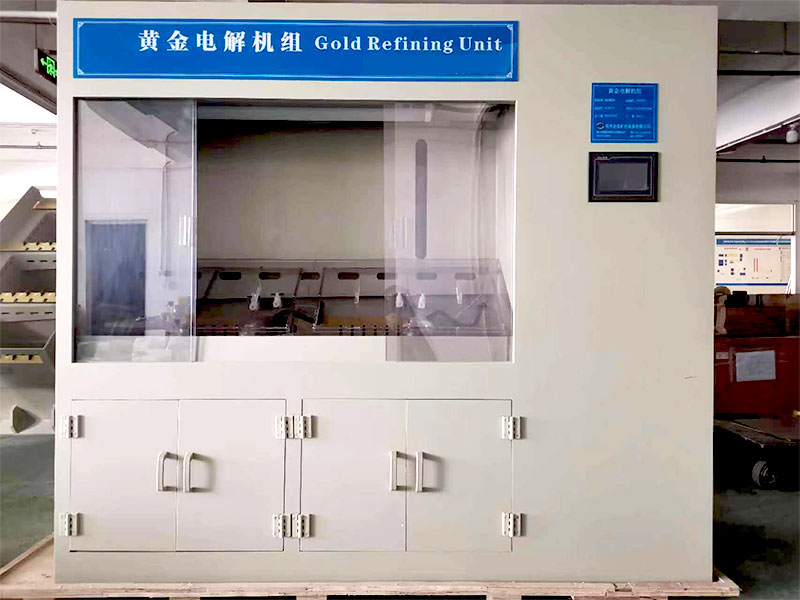
- Electrowinning:
- Electrowinning is a technique used to recover gold from the cyanide solution after leaching. An electric current is passed through the solution, causing gold to deposit onto electrodes. This method is efficient and results in high-purity gold.
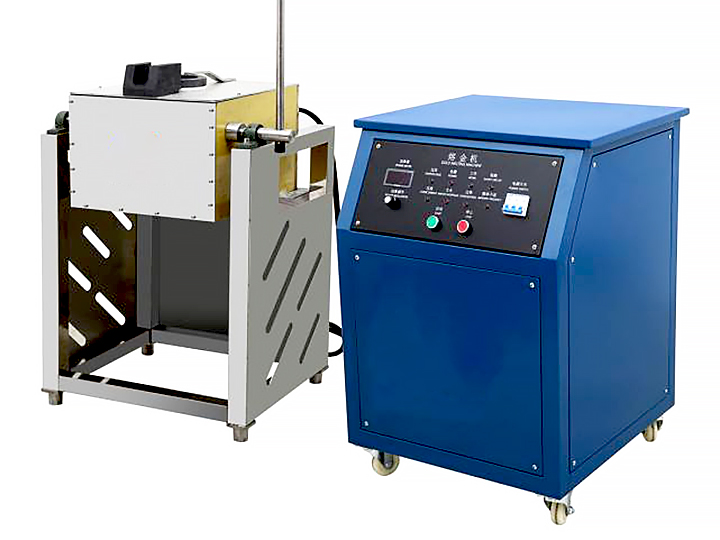
- Smelting and Refining:
- The final step in processing and refining gold is smelting, where the gold is heated to its melting point and combined with fluxes to remove impurities. The molten gold is then poured into molds to form ingots or bars. Further refining techniques, such as the Miller process or Wohlwill process, may be employed to achieve the highest levels of purity.
Applications of Processed and Refined Gold
Processed and refined gold finds use in a wide array of industries, thanks to its high purity, durability, and other desirable properties.
- Jewelry:
- The most common use of refined gold is in the creation of jewelry. The metal’s luster, malleability, and resistance to tarnish make it ideal for crafting various types of jewelry, from rings and necklaces to intricate designs.
- Electronics:
- In the electronics industry, gold is prized for its excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion. It is used in the manufacture of connectors, switches, and other critical components in devices such as smartphones, computers, and medical equipment.
- Finance and Investment:
- Gold bars, coins, and other forms of bullion are often used as investment vehicles. Investors buy refined gold as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty. Central banks also hold significant reserves of gold as part of their monetary policies.
- Medical and Dental Applications:
- Refined gold is used in dentistry for crowns, bridges, and other dental work due to its biocompatibility and non-reactive nature. Additionally, gold is used in some medical devices and treatments, including certain types of cancer therapy.
Industry Insights and Future Trends in Gold Processing and Refining
The gold processing and refining industry is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and changing market dynamics.
- Technological Innovations:
- The industry is seeing a shift towards more efficient and environmentally friendly methods of processing and refining gold. Innovations such as bioleaching, which uses bacteria to leach gold from ores, are gaining traction as sustainable alternatives to traditional methods.
- Sustainability Initiatives:
- As environmental regulations become stricter, the gold refining industry is adopting greener practices. This includes reducing the use of hazardous chemicals, improving waste management, and sourcing gold from ethically responsible mines.
- Market Dynamics:
- The global demand for gold continues to rise, driven by increasing consumption in emerging markets and the growing popularity of gold as an investment. This trend is expected to sustain the demand for processing and refining gold in the foreseeable future.
Processing and refining gold is a complex and vital process that transforms raw ore into pure, high-quality gold. With various techniques available, the industry ensures that gold is efficiently extracted, refined, and prepared for its many applications. As technology and sustainability practices advance, the gold processing and refining industry will continue to play a crucial role in meeting the global demand for this precious metal.