refining gold from electronics


Refining Gold from Electronics: A Comprehensive Guide
As the world increasingly relies on electronic devices, a significant amount of precious metals like gold are used in their manufacturing. From smartphones to computers, many electronic components contain small quantities of gold due to its excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion. Recovering and refining gold from electronics has become an important process, both for sustainability and profit. This article will explore the methods and tools needed to extract and refine gold from discarded electronics.
Why Gold is Used in Electronics
Gold is a preferred metal in electronics because of its excellent electrical conductivity, resistance to tarnishing, and ability to maintain a stable connection. It is primarily found in connectors, circuit boards, CPUs, and memory chips. Despite being present in tiny amounts, when collected from multiple devices, the cumulative gold content can be substantial, making it worthwhile to refine.


Steps for Refining Gold from Electronics
Step 1: Collect the Electronic Devices
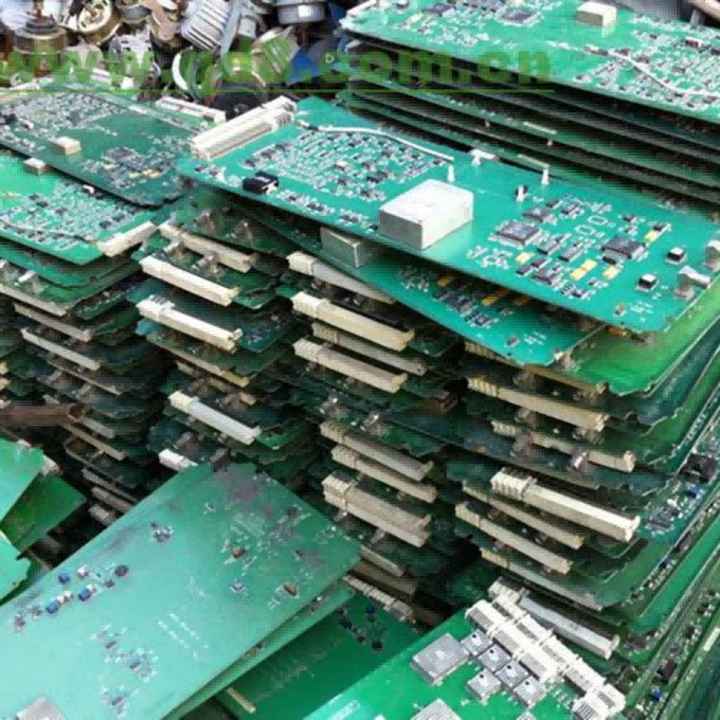
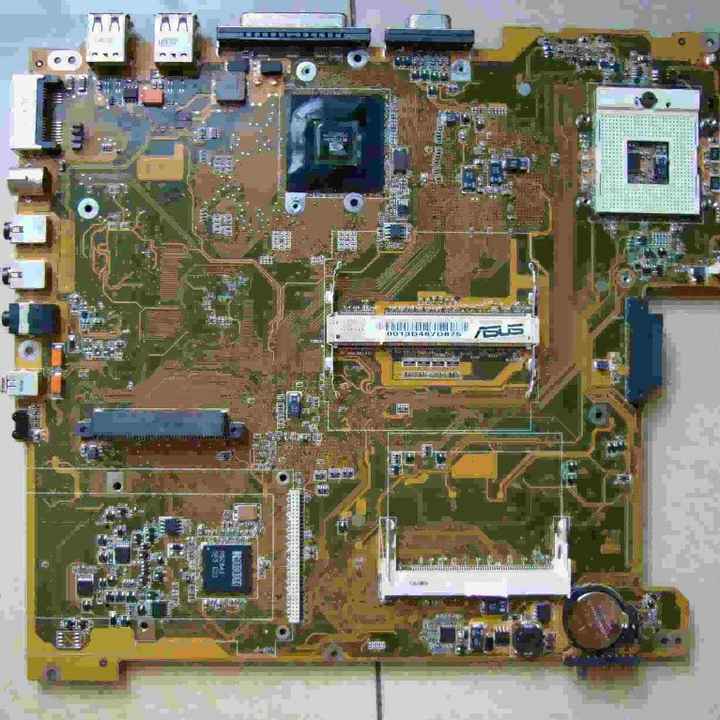
The first step in refining gold from electronics is to gather devices that contain gold. These include items such as:
- Old computers and laptops (especially motherboards, CPUs, and RAM sticks)
- Cell phones (older models often have more gold)
- Printers and scanners
- Television circuit boards
- Other small electronic devices
Once collected, disassemble these items to separate the gold-containing components, such as connectors, pins, and circuit boards.
Step 2: Use Protective Gear
Before starting the gold refining process, it’s crucial to use proper protective gear. Refining gold from electronics involves handling dangerous chemicals like nitric acid and aqua regia, which can cause burns, release toxic fumes, and are harmful if inhaled or touched.
Recommended protective gear includes:
- Chemical-resistant gloves
- Safety goggles
- Respirator mask (for fumes)
- Protective clothing
- A well-ventilated workspace or fume hood
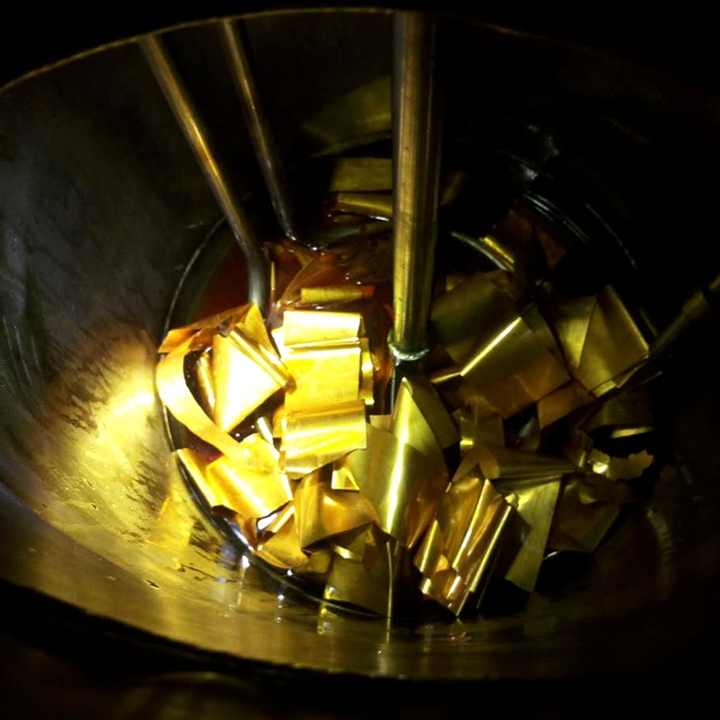
Step 3: Prepare the Gold-Plated Parts
Once you’ve disassembled the devices, extract the gold-plated components. These can include the gold pins, connectors, and other small parts found in circuit boards. Carefully cut or remove these parts and place them in a container, ready for the refining process.
Step 4: Dissolving Non-Gold Materials with Aqua Regia
The refining process typically uses a combination of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, known as aqua regia. Aqua regia dissolves the base metals, leaving behind the gold. Here’s how you can proceed:
- Place the gold-plated parts into a glass container.
- Slowly add nitric acid and then hydrochloric acid to form aqua regia.
- Let the solution sit until all the non-gold materials are dissolved.
This process may take several hours or days, depending on the volume of material.
Step 5: Filter the Solution
Once the base metals are dissolved, the remaining solution will contain dissolved gold and other impurities. Use a fine filter to separate the solid gold particles from the liquid. After filtration, only gold remains in the filter, while the dissolved metals stay in the solution.
Step 6: Precipitating the Gold
To precipitate the gold from the solution, you can add a reducing agent, such as sodium metabisulfite or ferrous sulfate, to the filtered solution. This causes the gold to fall out of the solution as a fine powder, which can then be collected.
Step 7: Rinse and Dry the Gold
After precipitating the gold, rinse it with distilled water to remove any remaining acid or impurities. Be sure to rinse thoroughly until the water is clear. Afterward, allow the gold powder to dry completely before proceeding to the final step.
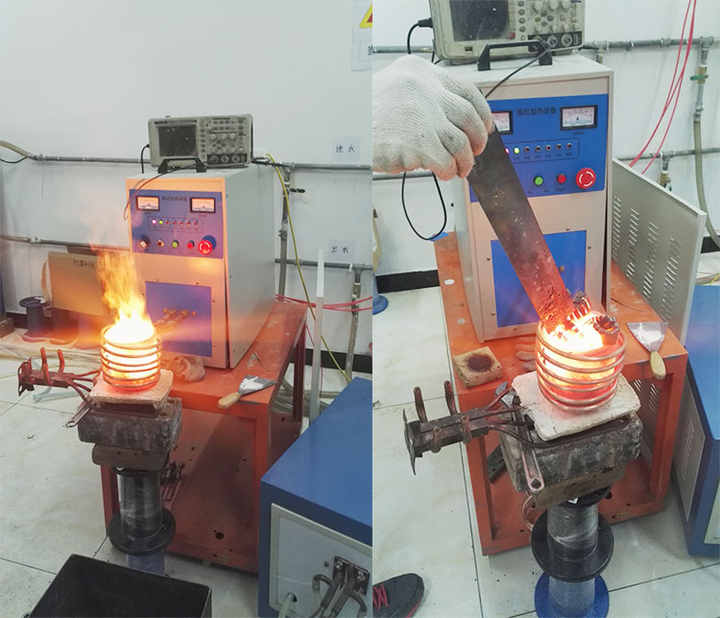
Step 8: Melt the Gold
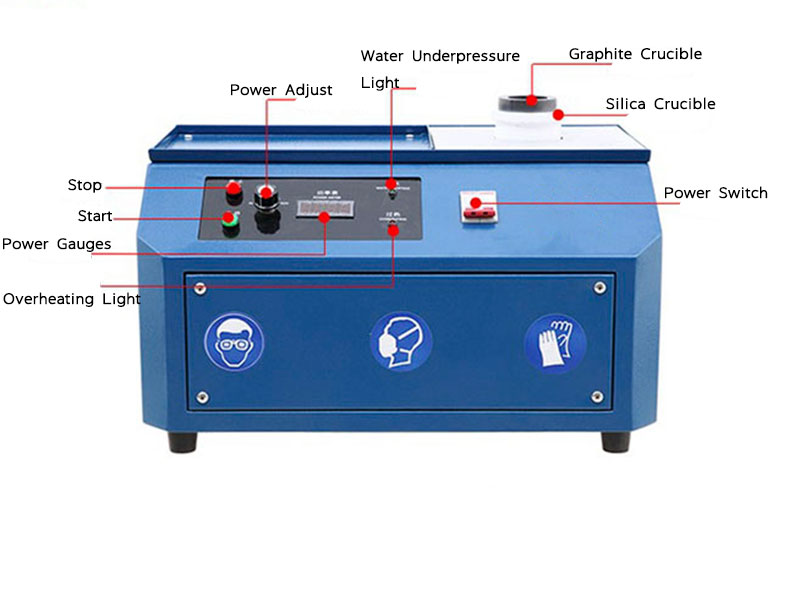
The last step in the refining process is to melt the gold powder into a solid form. This can be done using a high-temperature furnace or a propane torch. Once melted, the gold can be cast into a mold to form bars, coins, or other shapes.
Safety Considerations in Refining Gold from Electronics
The process of refining gold from electronics involves hazardous chemicals, so safety should always be a top priority. Always ensure:
- Adequate ventilation to avoid exposure to harmful fumes.
- Proper disposal of used chemicals and materials in accordance with environmental regulations.
- Following strict safety protocols to avoid chemical burns and accidents.
Is Refining Gold from Electronics Profitable?
Refining gold from electronics can be profitable, especially when processing a large volume of devices. While individual devices may only contain small amounts of gold, when aggregated over time, the recovered gold can add up. However, the profitability depends on the scale of operation, cost of materials, and labor involved in refining.
The Environmental Benefits of Refining Gold from Electronics
In addition to being a potential source of profit, refining gold from electronics is an environmentally responsible practice. Recycling electronics reduces the need for mining and helps minimize electronic waste, which can be harmful to ecosystems if disposed of improperly.
Refining gold from electronics is a valuable and sustainable way to recover precious metals from discarded devices. While the process requires specialized tools, chemicals, and safety precautions, it offers both economic and environmental benefits. Whether for hobbyists or those involved in electronic waste recycling, refining gold from electronics can be a rewarding endeavor.