smelting gold ore
The Process of Smelting Gold Ore From Raw Material to Pure Gold
Gold ore smelting is a crucial step in the extraction of gold from its natural state. This process involves heating the ore to high temperatures to separate the gold from other minerals and impurities. In this article, we will explore the methods used in smelting gold ore, the equipment required, and the importance of safety and environmental considerations.
Understanding Smelting Gold Ore
Smelting gold ore is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of metallurgy and the physical properties of gold. The goal is to extract pure gold from the ore, which often contains a mix of other minerals and contaminants.
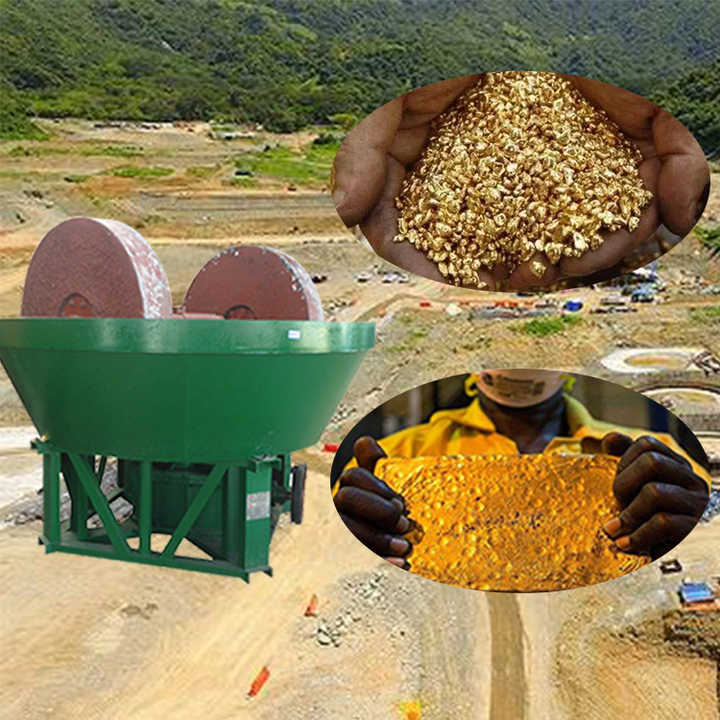
Preparation of Gold Ore
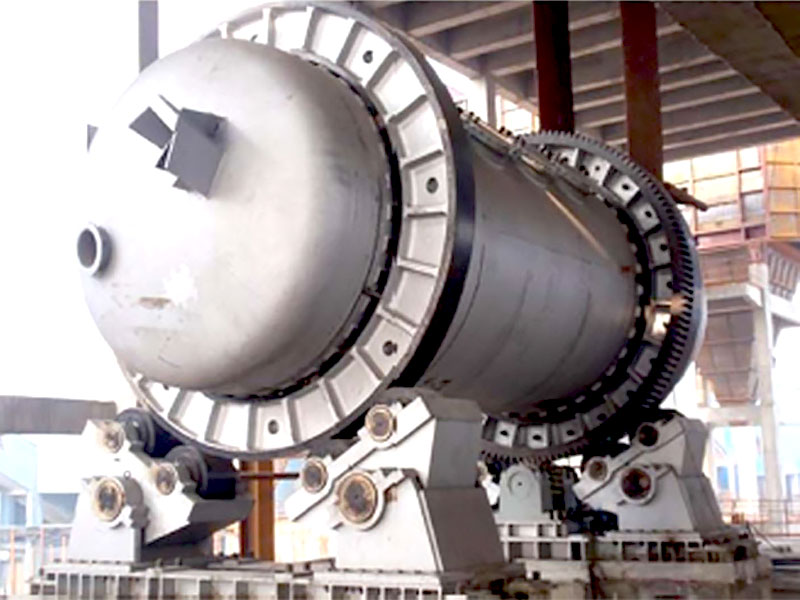
Before smelting can begin, the gold ore must be prepared. This involves crushing and grinding the ore into a fine powder to increase the surface area and make it easier for the gold particles to be separated from the surrounding rock. The size reduction is typically done using mechanical devices such as crushers and ball mills.
Roasting
Roasting is a preliminary step that involves heating the crushed ore to a high temperature in the presence of oxygen. This process helps to oxidize sulfides and other compounds that may interfere with the smelting process. Roasting can improve the efficiency of gold extraction by breaking down these compounds.
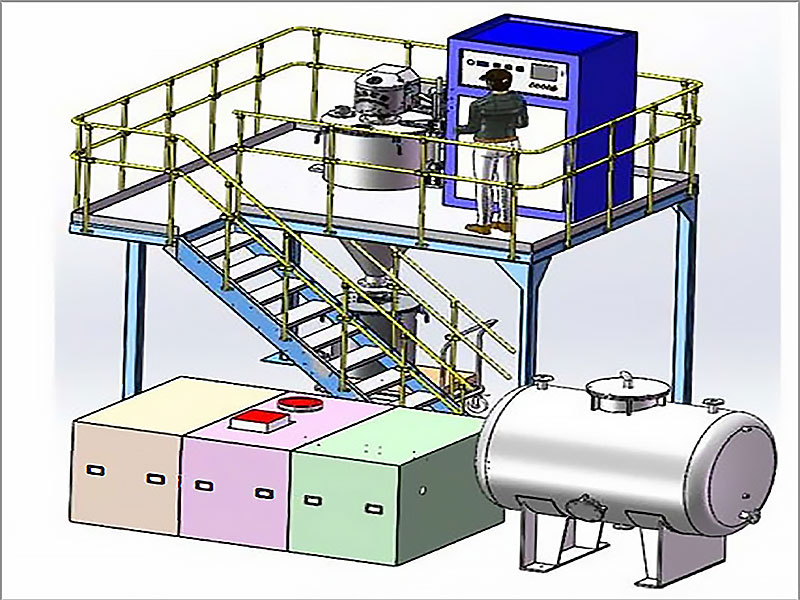
Smelting Process
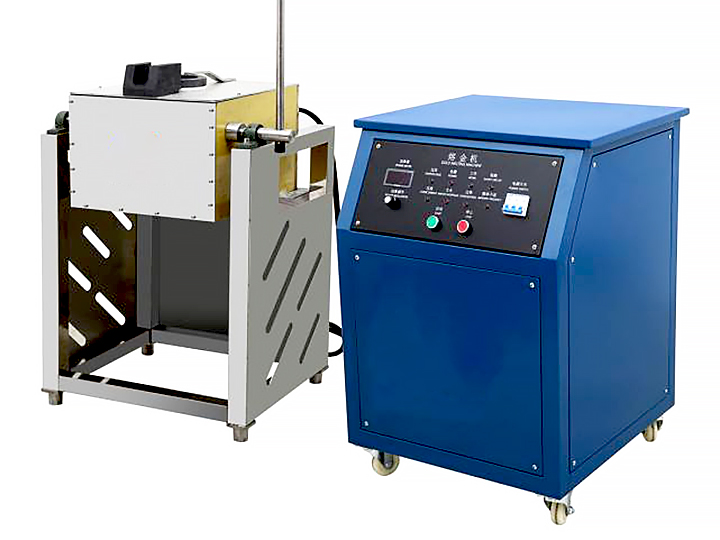
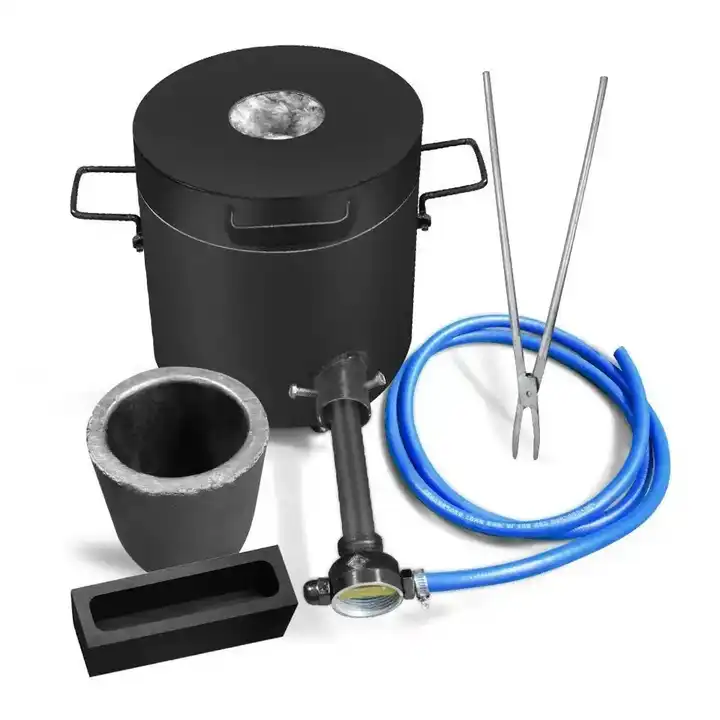
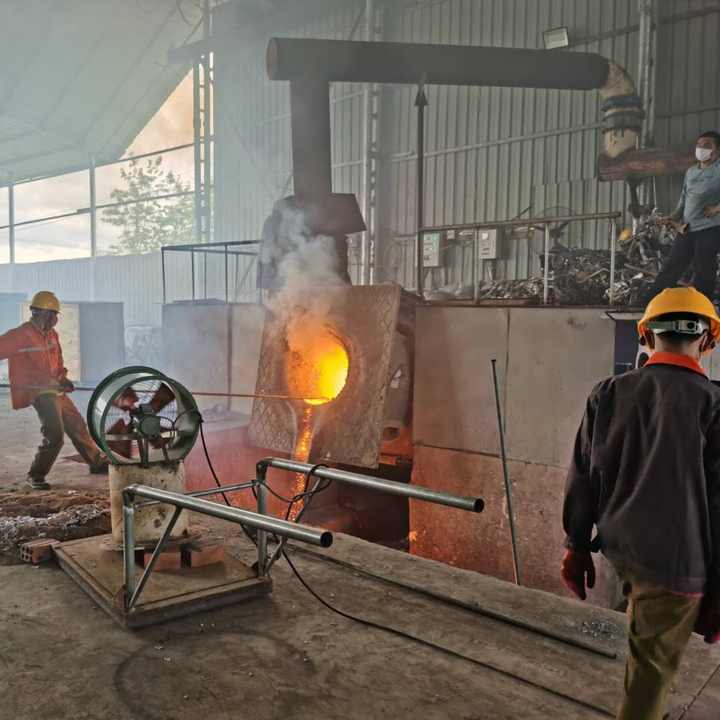
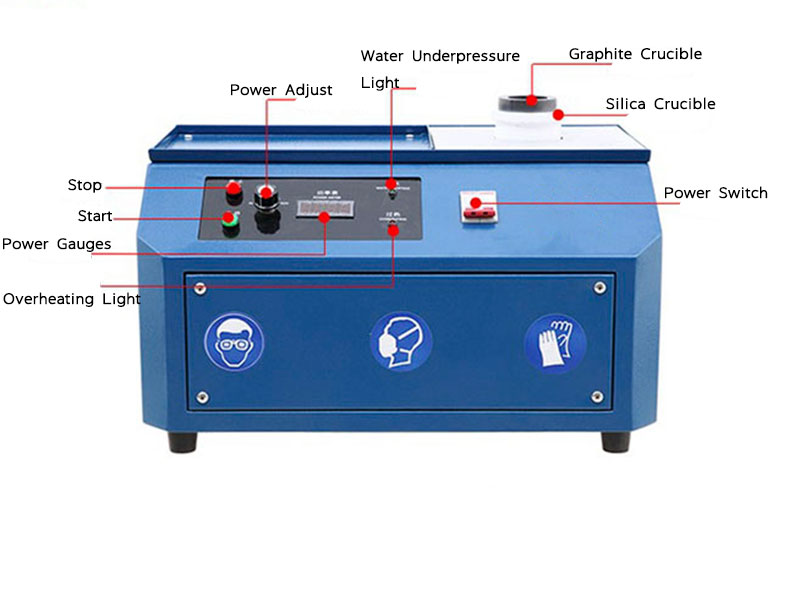
Furnace Setup
The smelting process begins by placing the prepared gold ore into a furnace. The furnace must be capable of reaching temperatures above the melting point of gold, which is approximately 1,064°C (1,947°F). Common types of furnaces used for smelting gold ore include electric arc furnaces and reverberatory furnaces.
Addition of Flux
Flux is added to the furnace to help separate the gold from impurities. Borax is a common flux used in small-scale operations because it lowers the melting point of slag and helps to float it off the top of the molten gold. Other fluxes include lime and silica.
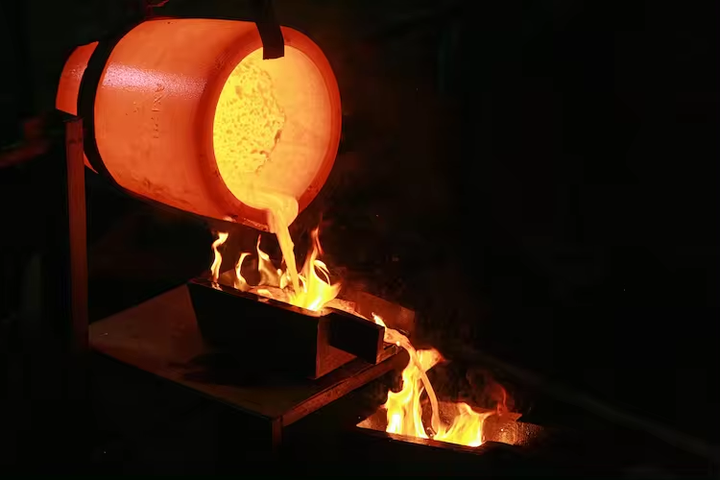
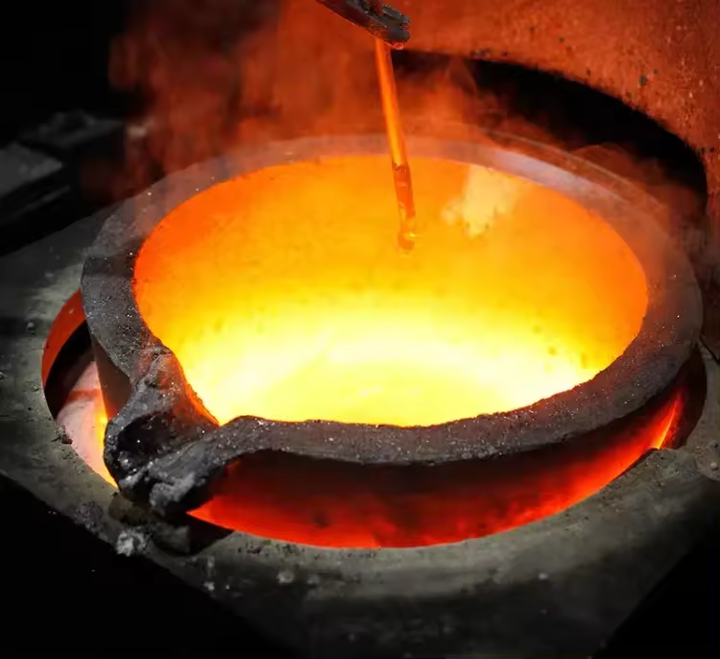
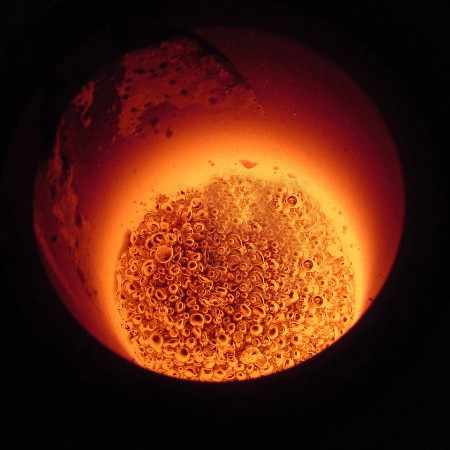
Melting and Separation
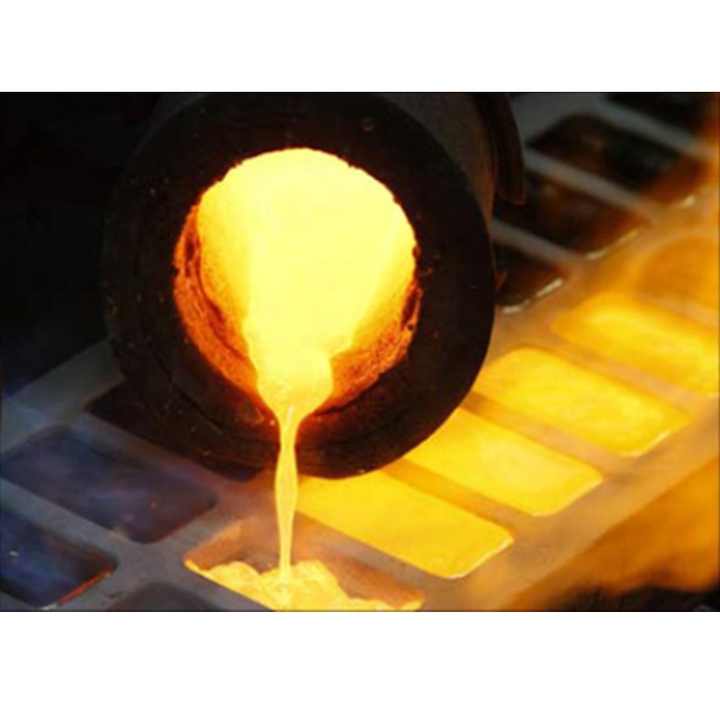
As the furnace heats up, the gold melts and separates from the slag. The slag, a mixture of impurities and flux, floats to the top of the molten gold. This layer is periodically removed, leaving behind the molten gold, which is then poured into molds to cool and solidify.
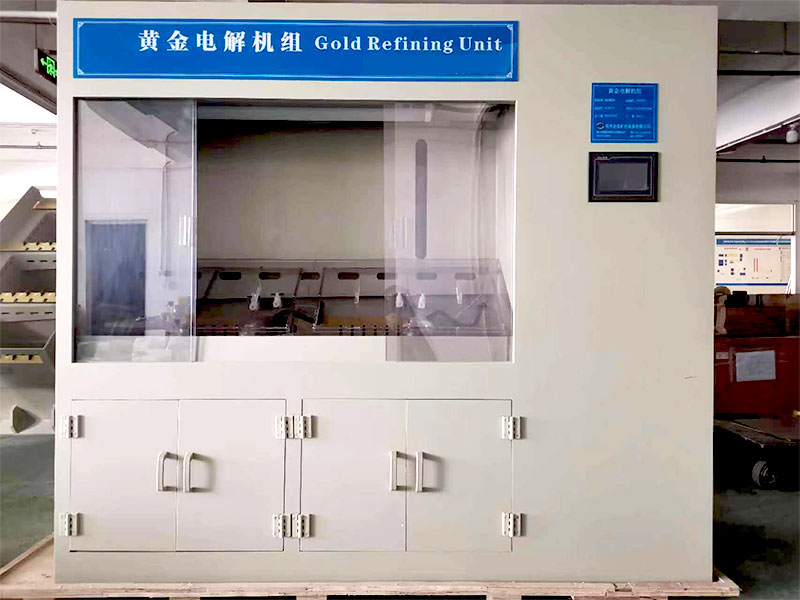
Post-Smelting Refinement
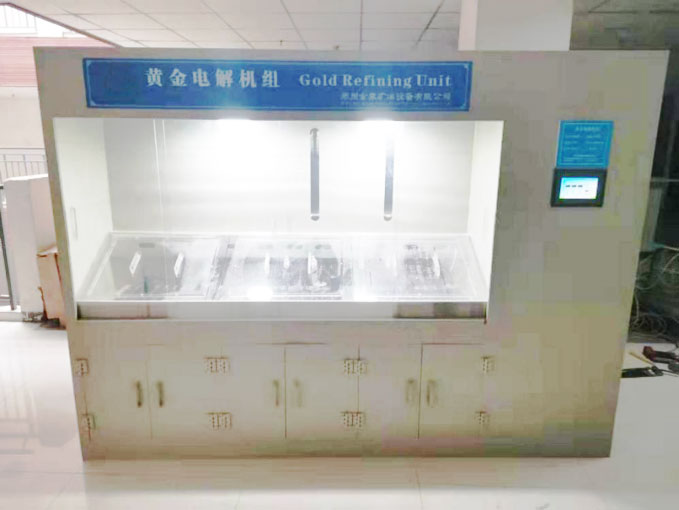
After smelting, the gold may still contain impurities that need to be removed. Further refinement can be achieved through processes such as electrolysis or chemical leaching. These methods can increase the purity of the gold to near-bullion standards.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Smelting gold ore presents several safety and environmental challenges. High temperatures and the use of chemicals can pose risks to operators. Proper protective gear, including heat-resistant clothing and respiratory protection, is essential. Ventilation systems should be in place to manage fumes and prevent the inhalation of toxic gases.
From an environmental perspective, smelting operations must adhere to strict regulations to minimize pollution. Waste materials, such as slag, should be disposed of responsibly to avoid contamination of soil and water.
Smelting gold ore is a fundamental process in the extraction of this precious metal. It requires specialized knowledge, equipment, and adherence to safety and environmental protocols. By understanding the steps involved in smelting gold ore, from preparation to final refinement, one can appreciate the complexity and skill required to transform raw ore into pure gold. As the demand for gold continues to grow, so does the importance of efficient and responsible smelting practices.